Evaluation of the teratogenic effects of three traditional Chinese medicines, Si Jun Zi Tang, Liu Jun Zi Tang and Shenling Baizhu San, during zebrafish pronephros development
- PMID: 26441476
- PMCID: PMC4588208
- DOI: 10.1293/tox.2013-0045
Evaluation of the teratogenic effects of three traditional Chinese medicines, Si Jun Zi Tang, Liu Jun Zi Tang and Shenling Baizhu San, during zebrafish pronephros development
Erratum in
-
Errata (Printer's correction).J Toxicol Pathol. 2016 Jan;29(1):74. Epub 2016 Feb 17. J Toxicol Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26989306 Free PMC article.
Abstract
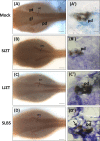
The aim of this study was to evaluate the teratogenic effects of three common Chinese medical prescriptions, Si Jun Zi Tang (SJZT), Liu Jun Zi Tang (LJZT) and Shenling Baizhu San (SLBS), during zebrafish pronephros development. We used the transgenic zebrafish line Tg(wt1b:EGFP) to assess the teratogenic effects using 12 different protocols, which comprised combinations of 4 doses (0, 25, 250, 1,250 ng/mL) and 3 exposure methods [methods I, 12-36 hours post fertilization (hpf), II, 24-48 hpf, and III, 24-36 hpf]. As a result, few defects in the kidneys were observed in the embryos exposed to 25 ng/mL of each medical prescription. The percentage of kidney malformation phenotypes increased as the exposure concentrations increased (25 ng/mL, 0-10%; 250 ng/mL, 0-60%; 1,250 ng/mL, 80-100%). Immunohistochemistry for α6F, which is a basolateral and renal tubular differentiation marker, revealed no obvious defective phenotypes in either SJZT- or LJZT-treated embryos, indicating that these Chinese medical prescriptions had minimal adverse effects on the pronephric duct. However, SLBS-treated embryos displayed a defective phenotype in the pronephric duct. According to these findings, we suggest (1) that the Chinese medical prescriptions induced kidney malformation phenotypes that are dose dependent and (2) that the embryonic zebrafish kidney was more sensitive to SLBS than SJZT and LJZT.
Keywords: Chinese medical prescriptions; kidney; nephrotoxicity; zebrafish.
Figures
References
-
- Long Z, Li Q, and Liu Z. Formulas of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Academy Press, Beijing University of Traditional Medicine. 2005.
-
- Hsu HY, Yang JJ, Lian SL, Ho YH, and Lin CC. Recovery of the hematopoietic system by Si-Jun-Zi-Tang in whole body irradiated mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 54: 69–75. 1996. - PubMed
-
- Liu L, Han L, Wong DYL, Yue PYK, Ha WY, Hu YH, Wang PX, and Wong RNS. Effects of Si-Jun-Zi decoction polysaccharides on cell migration and gene expression in wounded rat intestinal epithelial cells. Br J Nutr. 93: 21–29. 2005. - PubMed
-
- Ozaki M, Nagatomo T, Maeda T, Kishioka S, and Yamamoto H. Pharmacological differences between Liu-Jun-Zi-Tang, a traditional Chinese herbal medicine, and domperidone on isolated guinea-pig ileum. Biol Pharm Bull. 29: 1349–1354. 2006. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
