Comparison of changes in urinary and blood levels of biomarkers associated with proximal tubular injury in rat models
- PMID: 26441477
- PMCID: PMC4588209
- DOI: 10.1293/tox.2014-0039
Comparison of changes in urinary and blood levels of biomarkers associated with proximal tubular injury in rat models
Erratum in
-
Errata (Printer's correction).J Toxicol Pathol. 2016 Jan;29(1):74. Epub 2016 Feb 17. J Toxicol Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26989306 Free PMC article.
Abstract
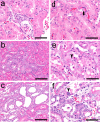
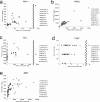
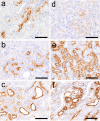
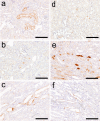
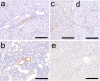
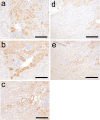
To investigate useful biomarkers associated with proximal tubular injury, we assessed changes in levels of a focused set of biomarkers in urine and blood. Male rats administered a single dose or four doses of gentamicin (GM, 240 mg/kg/day) or a single dose of cisplatin (CDDP, 5 mg/kg) were euthanized on days 2 (the day after initial dosing) 5, or 12. At each time point, histopathological examination of the kidney and immunohistochemistry for biomarkers, kidney injury molecule-1 (Kim-1), lipocalin (NGAL), clusterin (CLU), cystatin C (CysC) and β2-microglobulin (β2M) were performed. Biomarker levels were measured in urine and blood. In both treatment groups, degenerated/necrotic proximal tubules and regenerated tubules were mainly observed on days 5 and 12, respectively. At the same time as these tubular injuries, urinary Kim-1, CysC and β2M levels were increased. Moreover, urinary levels of CysC and β2M in GM-treated animals and Kim-1 in CDDP-treated animals increased (on day 2) prior to tubular injury on day 5. This was considered to reflect the characteristics of drug toxicity. Although almost all of the biomarkers in blood were not sufficiently sensitive to detect proximal tubular injury, urinary and plasma β2M levels simultaneously increased. Therefore, in addition to urinary Kim-1, CysC and β2M levels, plasma β2M levels were also considered useful for detecting proximal tubular injury.
Keywords: biomarker; cisplatin; gentamicin; immunohistochemistry; kidney; proximal tubular injury.
Figures


References
-
- Naughton CA. Drug-induced nephrotoxicity. Am Fam Physician. 78: 743–750. 2008. - PubMed
-
- Redfern WS, Ewart L, Hammond TG, Bialecki R, Kinter L, Lindgren S, Pollard CE, Roberts R, Rolf MG, and Valentin JP. Impact and frequency of different toxicities throughout the pharmaceutical life cycle. Toxicologist. 114: 1081 2010.
-
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Seven biomarkers of drug-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. 2008, from website: http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/DrugDevelopmentTools....
-
- FDA Non-clinical qualification of urinary biomarkers of nephrotoxicity. HESI nephrotoxicity qualification. 2010, from website: http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/DrugDevelopmentTools....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
