Activated regulatory T cell regulates neural stem cell proliferation in the subventricular zone of normal and ischemic mouse brain through interleukin 10
- PMID: 26441532
- PMCID: PMC4568339
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00361
Activated regulatory T cell regulates neural stem cell proliferation in the subventricular zone of normal and ischemic mouse brain through interleukin 10
Abstract
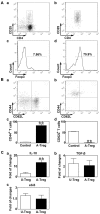
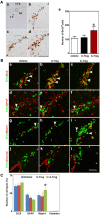
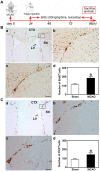
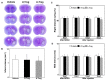
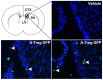
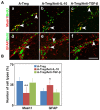
Recent studies have demonstrated that the depletion of Regulatory T cells (Tregs) inhibits neural progenitor cell migration after brain ischemia. However, whether Tregs affect neural stem/progenitor cell proliferation is unclear. We explored the effect of Tregs on neurogenesis in the subventricular zone (SVZ) after ischemia. Tregs were isolated and activated in vitro. Adult male C57BL/6 mice underwent 60 min transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO). Then Tregs (1 × 10(5)) were injected into the left lateral ventricle (LV) of normal and ischemic mouse brain. Neurogenesis was determined by immunostaining. The mechanism was examined by inhibiting interleukin 10 (IL-10) and transforming growth factor (TGF-β) signaling. We found that the number of BrdU(+) cells in the SVZ was significantly increased in the activated Tregs-treated mice. Double immunostaining showed that these BrdU(+) cells expressed Mash1. Blocking IL-10 reduced the number of Mash1(+)/BrdU(+) cells, but increased the amount of GFAP(+)/BrdU(+) cells. Here, we conclude that activated Tregs enhanced neural stem cell (NSC) proliferation in the SVZ of normal and ischemic mice; blockage of IL-10 abolished Tregs-mediated NSC proliferation in vivo and in vitro. Our results suggest that activated Tregs promoted NSC proliferation via IL-10, which provides a new therapeutic approach for ischemic stroke.
Keywords: brain ischemia; interleukin 10; neurogenesis; regulatory T cell; subventricular zone.
Figures


References
-
- Barrat F. J., Cua D. J., Boonstra A., Richards D. F., Crain C., Savelkoul H. F., et al. . (2002). In vitro generation of interleukin 10-producing regulatory CD4(+) T cells is induced by immunosuppressive drugs and inhibited by T helper type 1 (Th1)- and Th2-inducing cytokines. J. Exp. Med. 195, 603–616. 10.1084/jem.20011629 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

