Ongoing burden of disease and mortality from HIV/CMV coinfection in Africa in the antiretroviral therapy era
- PMID: 26441939
- PMCID: PMC4585099
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01016
Ongoing burden of disease and mortality from HIV/CMV coinfection in Africa in the antiretroviral therapy era
Abstract
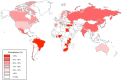
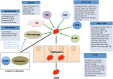
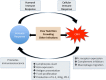
Human Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a well-recognized pathogen in the context of HIV infection, but since the roll out of ART, clinical and scientific interest in the problem of HIV/CMV coinfection has diminished. However, CMV remains a significant cofactor in HIV disease, with an influence on HIV acquisition, disease progression, morbidity, and mortality. Disease manifestations may be a result of direct interplay between the two viruses, or may arise as a secondary consequence of immune dysregulation and systemic inflammation. The problem is most relevant when the rates of coinfection are high, most notably in sub-Saharan Africa, and in children at risk of acquiring both infections early in life. Understanding the interplay between these viruses and developing strategies to diagnose, treat and prevent CMV should be a priority.
Keywords: CMV; HIV-1; antiretroviral therapy; coinfection; immune activation; pediatric infectious diseases; sub-Saharan Africa.
Figures
References
-
- Alao O. O., Mamman A., Araoye M. O., Joseph E. (2009). Effect of demographic variables on cytomegalovirus antibody seropositivity among prospective blood donors in Jos, Nigeria. Niger. Postgrad. Med. J. 16, 139–142. - PubMed
-
- Böhler T., Wintergerst U., Linde R., Belohradsky B. H., Debatin K. M. (2001). CD95 (APO-1/Fas) expression on naive CD4(+) T cells increases with disease progression in HIV-infected children and adolescents: effect of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). Pediatr. Res. 49, 101–110. 10.1203/00006450-200101000-00021 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

