Differential expression of seven conserved microRNAs in response to abiotic stress and their regulatory network in Helianthus annuus
- PMID: 26442054
- PMCID: PMC4585256
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00741
Differential expression of seven conserved microRNAs in response to abiotic stress and their regulatory network in Helianthus annuus
Abstract
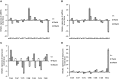
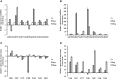
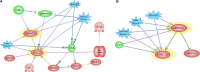
Biotic and abiotic stresses affect plant development and production through alternation of the gene expression pattern. Gene expression itself is under the control of different regulators such as miRNAs and transcription factors (TFs). MiRNAs are known to play important roles in regulation of stress responses via interacting with their target mRNAs. Here, for the first time, seven conserved miRNAs, associated with drought, heat, salt and cadmium stresses were characterized in sunflower. The expression profiles of miRNAs and their targets were comparatively analyzed between leaves and roots of plants grown under the mentioned stress conditions. Gene ontology analysis of target genes revealed that they are involved in several important pathways such as auxin and ethylene signaling, RNA mediated silencing and DNA methylation processes. Gene regulatory network highlighted the existence of cross-talks between these stress-responsive miRNAs and the other stress responsive genes in sunflower. Based on network analysis, we suggest that some of these miRNAs in sunflower such as miR172 and miR403 may play critical roles in epigenetic responses to stress. It seems that depending on the stress type, theses miRNAs target several pathways and cellular processes to help sunflower to cope with drought, heat, salt and cadmium stress conditions in a tissue-associated manner.
Keywords: abiotic stress; miRNA; regulatory network; sunflower (Helianthus annuus).
Figures




Similar articles
-
MicroRNA expression patterns unveil differential expression of conserved miRNAs and target genes against abiotic stress in safflower.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 18;15(2):e0228850. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228850. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32069300 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic regulatory networks mediated by microRNAs and transcription factors under drought, heat and salt stresses in Oryza Sativa spp.Gene. 2015 Jan 25;555(2):127-39. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.10.054. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Gene. 2015. PMID: 25445270
-
Genome-wide identification and in-silico expression analysis of CCO gene family in sunflower (Helianthus annnus) against abiotic stress.Plant Mol Biol. 2024 Apr 3;114(2):34. doi: 10.1007/s11103-024-01433-0. Plant Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38568355 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA: a new target for improving plant tolerance to abiotic stress.J Exp Bot. 2015 Apr;66(7):1749-61. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv013. Epub 2015 Feb 19. J Exp Bot. 2015. PMID: 25697792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNAs: Major modulators for crop growth and development under abiotic stresses.Biotechnol Lett. 2017 May;39(5):685-700. doi: 10.1007/s10529-017-2302-9. Epub 2017 Feb 25. Biotechnol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28238061 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of the APETALA2/Ethylene-responsive factor (AP2/ERF) transcription factor family in sunflower.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 1;8(1):11576. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29526-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30068961 Free PMC article.
-
In silico search and biological validation of microRNAs related to drought response in peach and almond.Funct Integr Genomics. 2017 May;17(2-3):189-201. doi: 10.1007/s10142-016-0488-x. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Funct Integr Genomics. 2017. PMID: 27068847
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of DCL, AGO, and RDR Gene Families in Pepper (Capsicum Annuum L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 30;19(4):1038. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041038. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29601523 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-Mediated Responses to Cadmium Stress in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plants (Basel). 2021 Jan 10;10(1):130. doi: 10.3390/plants10010130. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33435199 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of small RNAs during cold acclimation in Arabidopsis thaliana.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Jun 29;20(1):298. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02511-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 32600430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alimohammadi A., Shiran B., Martinez-Gomez P., Ebrahimie E. (2013). Identification of water-deficit resistance genes in wild almond Prunus scoparia using cDNA-AFLP. Sci. Hortic. 159, 19–28. 10.1016/j.scienta.2013.04.023 - DOI
-
- Čatský J. (1960). Determination of water deficit in disks cut out from leaf blades. Biol. Plant 2, 76–78. 10.1007/BF02920701 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

