Kupffer's vesicle size threshold for robust left-right patterning of the zebrafish embryo
- PMID: 26442502
- PMCID: PMC5434515
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.24355
Kupffer's vesicle size threshold for robust left-right patterning of the zebrafish embryo
Abstract
Background: Motile cilia in the "organ of asymmetry" create directional fluid flows that are vital for left-right (LR) asymmetric patterning of vertebrate embryos. Organ function often depends on tightly regulated organ size control, but the role of organ of asymmetry size in LR patterning has remained unknown. Observations of the organ of asymmetry in the zebrafish, called Kupffer's vesicle (KV), have suggested significant variations in KV size in wild-type embryos, raising questions about the impact of KV organ size on LR patterning.
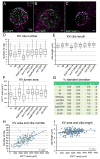
Results: To understand the relationship between organ of asymmetry size and its function, we characterized variations in KV at several developmental stages and in several different zebrafish strains. We found that the number of KV cilia and the size of the KV lumen were highly variable, whereas the length of KV cilia showed less variation. These variabilities were similar among different genetic backgrounds. By specifically modulating KV size and analyzing individual embryos, we identified a size threshold that is necessary for KV function.
Conclusions: Together these results indicate the KV organ of asymmetry size is not tightly controlled during development, but rather must only exceed a threshold to direct robust LR patterning of the zebrafish embryo.
Keywords: cilia; congenital disease; developmental noise; left-right patterning; organ size control.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Kupffer's vesicle is a ciliated organ of asymmetry in the zebrafish embryo that initiates left-right development of the brain, heart and gut.Development. 2005 Mar;132(6):1247-60. doi: 10.1242/dev.01663. Epub 2005 Feb 16. Development. 2005. PMID: 15716348
-
The Rho kinase Rock2b establishes anteroposterior asymmetry of the ciliated Kupffer's vesicle in zebrafish.Development. 2011 Jan;138(1):45-54. doi: 10.1242/dev.052985. Epub 2010 Nov 23. Development. 2011. PMID: 21098560 Free PMC article.
-
Organized chaos in Kupffer's vesicle: how a heterogeneous structure achieves consistent left-right patterning.Bioarchitecture. 2014;4(3):119-25. doi: 10.4161/19490992.2014.956593. Bioarchitecture. 2014. PMID: 25454897 Free PMC article.
-
Salient features of the ciliated organ of asymmetry.Bioarchitecture. 2014 Jan-Feb;4(1):6-15. doi: 10.4161/bioa.28014. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Bioarchitecture. 2014. PMID: 24481178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cilia in vertebrate left-right patterning.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016 Dec 19;371(1710):20150410. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0410. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27821522 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding laterality disorders and the left-right organizer: Insights from zebrafish.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Dec 23;10:1035513. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1035513. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36619867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physical limits of flow sensing in the left-right organizer.Elife. 2017 Jun 14;6:e25078. doi: 10.7554/eLife.25078. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28613157 Free PMC article.
-
Emx2 is an essential regulator of ciliated cell development across embryonic tissues.iScience. 2024 Oct 28;27(12):111271. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111271. eCollection 2024 Dec 20. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39687012 Free PMC article.
-
3D viscoelastic drag forces contribute to cell shape changes during organogenesis in the zebrafish embryo.Cells Dev. 2021 Dec;168:203718. doi: 10.1016/j.cdev.2021.203718. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Cells Dev. 2021. PMID: 34273601 Free PMC article.
-
Meteorins regulate the formation of the left-right organizer and the establishment of vertebrate body asymmetry.Elife. 2025 Aug 1;14:RP105430. doi: 10.7554/eLife.105430. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40748055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afzelius BA. A human syndrome caused by immotile cilia. Science. 1976;193:317–319. - PubMed
-
- Blum M, Weber T, Beyer T, Vick P. Evolution of leftward flow. Seminars in cell & developmental biology. 2009;20:464–471. - PubMed
-
- Bonetti M, Paardekooper Overman J, Tessadori F, Noel E, Bakkers J, den Hertog J. Noonan and LEOPARD syndrome Shp2 variants induce heart displacement defects in zebrafish. Development. 2014;141:1961–1970. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

