Influence of tumour stage at breast cancer detection on survival in modern times: population based study in 173,797 patients
- PMID: 26442924
- PMCID: PMC4595560
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.h4901
Influence of tumour stage at breast cancer detection on survival in modern times: population based study in 173,797 patients
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the influence of stage at breast cancer diagnosis, tumour biology, and treatment on survival in contemporary times of better (neo-)adjuvant systemic therapy.
Design: Prospective nationwide population based study.
Setting: Nationwide Netherlands Cancer Registry.
Participants: Female patients with primary breast cancer diagnosed between 1999 and 2012 (n=173,797), subdivided into two time cohorts on the basis of breast cancer diagnosis: 1999-2005 (n=80,228) and 2006-12 (n=93,569).
Main outcome measures: Relative survival was compared between the two cohorts. Influence of traditional prognostic factors on overall mortality was analysed with Cox regression for each cohort separately.
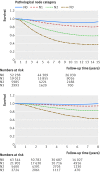
Results: Compared with 1999-2005, patients from 2006-12 had smaller (≤ T1 65% (n=60,570) v 60% (n=48,031); P<0.001), more often lymph node negative (N0 68% (n=63,544) v 65% (n=52,238); P<0.001) tumours, but they received more chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, and targeted therapy (neo-adjuvant/adjuvant systemic therapy 60% (n=56,402) v 53% (n=42,185); P<0.001). Median follow-up was 9.8 years for 1999-2005 and 3.9 years for 2006-12. The relative five year survival rate in 2006-12 was 96%, improved in all tumour and nodal stages compared with 1999-2005, and 100% in tumours ≤ 1 cm. In multivariable analyses adjusted for age and tumour type, overall mortality was decreased by surgery (especially breast conserving), radiotherapy, and systemic therapies. Mortality increased with progressing tumour size in both cohorts (2006-12 T1c v T1a: hazard ratio 1.54, 95% confidence interval 1.33 to 1.78), but without a significant difference in invasive breast cancers until 1 cm (2006-12 T1b v T1a: hazard ratio 1.04, 0.88 to 1.22), and independently with progressing number of positive lymph nodes (2006-12 N1 v N0: 1.25, 1.17 to 1.32).
Conclusions: Tumour stage at diagnosis of breast cancer still influences overall survival significantly in the current era of effective systemic therapy. Diagnosis of breast cancer at an early tumour stage remains vital.
© Saadatmand et al 2015.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at
Figures

References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 2015;65:5-29. - PubMed
-
- Cossetti RJ, Tyldesley SK, Speers CH, et al. Comparison of breast cancer recurrence and outcome patterns between patients treated from 1986 to 1992 and from 2004 to 2008. J Clin Oncol 2015;33:65-73. - PubMed
-
- DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin 2014;64:252-71. - PubMed
-
- Berry DA, Cronin KA, Plevritis SK, et al. Effect of screening and adjuvant therapy on mortality from breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2005;353:1784-92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
