Interventions for hidradenitis suppurativa
- PMID: 26443004
- PMCID: PMC6464653
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010081.pub2
Interventions for hidradenitis suppurativa
Abstract
Background: Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterised by recurrent painful boils in flexural sites, such as the axillae and groin, that affects about 1% of the population, with onset in early adulthood.
Objectives: To assess the effects of interventions for HS in people of all ages.
Search methods: We searched the following databases up to 13 August 2015: the Cochrane Skin Group Specialised Register, CENTRAL in the Cochrane Library (Issue 7, 2015), MEDLINE (from 1946), EMBASE (from 1974), and LILACS (from 1982). We also searched five trials registers and handsearched the conference proceedings of eight dermatology meetings. We checked the reference lists of included and excluded studies for further references to relevant trials.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of all interventions for hidradenitis suppurativa.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed study eligibility and methodological quality and performed data extraction. Our primary outcomes were quality of life, measured by a validated dermatology-specific scale, and adverse effects of the interventions.
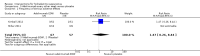
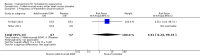
Main results: Twelve trials, with 615 participants, met our inclusion criteria. The median number of participants in each trial was 27, and median trial duration was 16 weeks. The included studies were conducted over a 32-year time period, from 1983 to 2015. A single RCT that was underpowered to detect clinically meaningful differences investigated most interventions.There were four trials of anti-TNF-α (tumour necrosis factor-alpha) therapies, which included etanercept, infliximab, and adalimumab. Adalimumab 40 mg weekly improved the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) score in participants with moderate to severe HS by 4.0 points relative to placebo (95% confidence interval (CI) -6.5 to -1.5 points), an effect size approximately equal to the DLQI minimal clinically important difference. We reduced the evidence quality to 'moderate' because the effect size was based on the results of only one study. In a meta-analysis of two studies with 124 participants, standard dose adalimumab 40 mg every other week was ineffective compared with placebo (moderate quality evidence). In a smaller study of 38 participants, of whom only 33 provided efficacy data, infliximab 5 mg/kg treatment improved DLQI by 8.4 DLQI points after eight weeks. Etanercept 50 mg twice weekly was well tolerated but ineffective.In a RCT of 200 participants, no difference was found in surgical complications (week one: risk ratio (RR) 0.78, 95% CI 0.58 to 1.05, moderate quality evidence) or risk of recurrence (after three months: RR 0.96, 95% CI 0.68 to 1.34, moderate quality evidence) in those randomised to receive a gentamicin-collagen sponge prior to primary closure compared with primary closure alone.RCTs of other interventions, including topical clindamycin 1% solution; oral tetracycline; oral ethinylestradiol 50 mcg with either cyproterone acetate 50 mg or norgestrel 500 mcg; intense pulsed light; neodymium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Nd:YAG) laser; methylene blue gel photodynamic therapy; and staphage lysate, were relatively small studies, preventing firm conclusions due to imprecision.
Authors' conclusions: Many knowledge gaps exist in RCT evidence for HS. Moderate quality evidence exists for adalimumab, which improves DLQI score when 40 mg is given weekly, twice the standard psoriasis dose. However, the 95% confidence interval includes an effect size of only 1.5 DLQI points, which may not be clinically relevant, and the safety profile of weekly dosing has not been fully established. Infliximab also improves quality of life, based on moderate quality evidence.More RCTs are needed in most areas of HS care, particularly oral treatments and the type and timing of surgical procedures. Outcomes should be validated, ideally, including a minimal clinically important difference for HS.
Conflict of interest statement
John R Ingram: John R Ingram is a local PI (principal investigator) for an observational study sponsored by AbbVie, manufacturers of adalimumab. He has not acted as a consultant for the manufacturer or taken part in paid Advisory Boards. Pick‐Ngor Woo: nothing to declare. Ser Ling Chua: nothing to declare. Anthony D Ormerod: nothing to declare. Nemesha Desai: "I have received consulting fees for advisory board work for AbbVie, which produces adalimumab." Anneke C Kai: nothing to declare. Kerry Hood: nothing to declare. Tara Burton: "I have received honorarium for speaking at AbbVie meetings in July 2014 and January 2015 about my personal patient journey. In June 2015, the HS Trust received a £5000 core funding grant from AbbVie, which produces adalimumab." Francisco Kerdel: "I have received honorariums for research or speaking agreements from Janssen Biotech, Inc., which produces Remicade® (infliximab); AbbVie, formally Abbott, which produces Humira® (adalimumab); and Amgen/Pfizer, which produces Enbrel® (etanercept)." Sarah E Garner: nothing to declare. Vincent Piguet: "I undertake personal advisory work with Pfizer, AbbVie, Janssen, Novartis, and Almirall. I have received support to my Department from AbbVie, Almirall, Alliance, Beiersdorf UK Ltd, Biotest, Celgene, Galderma, Genus Pharma, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Meda, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Sinclair Pharma, Spirit Pharmaceuticals, Stiefel, Sumed, and TyPham. The Department also received financial support from Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) copyright. Please note: adalimumab is produced by AbbVie; ustekinumab is produced by Janssen; infliximab is produced by MSD; and etanercept is produced by Pfizer."
Figures

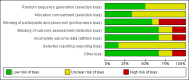
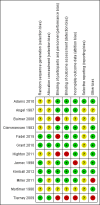












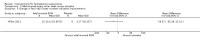



















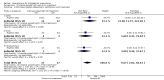




Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Adams 2010 {published data only}
-
- Adams DR, Yankura JA, Fogelberg AC, Anderson BE. Treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa with etanercept injection. Archives of Dermatology 2010;146(5):501‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Angel 1987 {published data only}
-
- Angel MF, Ramasastry SS, Manders EK, Ganfield D, Futrell JW. Beneficial effects of staphage lysate in the treatment of chronic recurrent hidradenitis suppurativa. Surgical Forum 1987;38:111‐2. [EMBASE: 1988094243]
Buimer 2008 {published data only}
-
- Buimer MG, Ankersmit MF, Wobbes T, Klinkenbijl JH. Surgical treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa with gentamicin sulfate: a prospective randomized study. Dermatologic Surgery 2008;34(2):224‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Clemmensen 1983 {published data only}
-
- Clemmensen OJ. Topical treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa with clindamycin. International Journal of Dermatology 1983;22(5):325‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fadel 2015 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Fadel MA, Tawfik AA. New topical photodynamic therapy for treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa using methylene blue niosomal gel: a single‐blind,randomized, comparative study. Clinical & Experimental Dermatology 2015;40(2):116‐22. [EMBASE: 2015763458] - PubMed
Grant 2010 {published data only}
-
- Grant A, Gonzalez T, Montgomery MO, Cardenas V, Kerdel FA. Infliximab therapy for patients with moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled crossover trial. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2010;62(2):205‐17. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Grant A, Kerdel FA, Gonzalez T. Long‐term efficacy and safety results (60 weeks) of a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, crossover trial of infliximab for patients with moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa. 67th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. AAD San Francisco, CA United States. Conference Start: 20090306 Conference End: 20090310. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2009;60(3 Suppl 1):AB106. [EMBASE: 70142143]
Highton 2011 {published data only}
-
- Highton L, Chan WY, Khwaja N, Laitung JK. Treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa with intense pulsed light: a prospective study. Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery 2011;128(2):459‐65. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Highton L, Laitung G, Khwaja N, Chan W‐Y, Chapel K, Bates K. Treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa using intense pulsed light. 29th Annual Conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery National Harbor, MD United States. Conference Start: 20090401 Conference End: 20090405. Lasers in Surgery and Medicine 2009;41:101. [EMBASE: 70332914]
Jemec 1998 {published data only}
-
- Jemec GB, Wendelboe P. Topical clindamycin versus systemic tetracycline in the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1998;39(6):971‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kimball 2012 {published data only}
-
- Gottlieb A, Menter A, Armstrong A, Cui N, Yamaguchi Y. Adalimumab treatment in women with moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa using a novel endpoint, HISCR (hidradenitis suppurativa clinical response): Analysis from the placebo‐controlled portion of a phase ii, randomized, double‐blind study. 61st Annual Scientific Meeting of the Society for Gynecologic Investigation, SGI 2014 Florence Italy. Conference Start: 20140326 Conference End: 20140329. Reproductive Sciences 2014;21(3 Suppl 1):220A‐221A. [EMBASE: 71380256]
-
- Gottlieb AB, Menter A, Belknap K, Chen K, Teixeira HD. Efficacy and safety of adalimumab treatment in women with moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa: Analysis from the placebo‐controlled portion of a phase ii, randomized, double‐blind study. 20th FIGO World Congress of Gynecology and Obstetrics Rome Italy. Conference Start: 20121007 Conference End: 20121012. International Journal of Gynaecology and Obstetrics 2012;119:S360. [EMBASE: 70905615]
-
- Jemec G, Sobell J, Scheinfeld N, Sood S, Gu Y. Efficacy results using a novel hidradenitis suppurativa endpoint, HiSCR (hidradenitis suppurativa clinical response), from the placebo‐controlled phase of a phase 2 adalimumab study. Conference: 72nd Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology Denver, CO United States. Conference Start: 20140321 Conference End: 20140325. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2014;70(5 Suppl 1):AB42. [EMBASE: 71390261]
-
- Kimball A, Jemec G, Okun M, Gu Y. Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in treatment of moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa: results from the placebo‐controlled portion of a phase ii, randomized, double‐blind study. Conference: 69th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology New Orleans, LA United States. Conference Start: 20110204 Conference End: 20110208. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2011;64(2 Suppl 1):AB155. [EMBASE: 70331898]
-
- Kimball A, Williams D, Jemec G, Gu Y. Efficacy and safety of adalimumab for moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa: Results from the open‐label phase of a 52‐week phase II, randomized, study. 70th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology San Diego, CA United States. Conference Start: 20120316 Conference End: 20120320. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2012;66(4 Suppl 1):AB50. [EMBASE: 70704053]
Miller 2011 {published data only}
-
- Miller I, Lynggaard CD, Lophaven S, Zachariae C, Dufour DN, Jemec GB. A double‐blind placebo‐controlled randomized trial of adalimumab in the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa. British Journal of Dermatology 2011;165(2):391‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mortimer 1986 {published data only}
-
- Mortimer PS, Dawber RP, Gales MA, Moore RA. A double‐blind controlled cross‐over trial of cyproterone acetate in females with hidradenitis suppurativa. British Journal of Dermatology 1986;115(3):263‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tierney 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hamzavi I, Mahmoud B, Tierney E, Hexsel C, Pui J, Ozog O. Prospective clinical and histopathologic study of hidradenitis suppurativa treated with laser. 29th Annual Conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery National Harbor, MD United States. Conference Start: 20090401 Conference End: 20090405. Lasers in Surgery and Medicine 2009;41:100. [EMBASE: 70332912]
-
- Mahmoud B, Hexsel C, Ozog D, Tierney E, Hamzavi I. Clinical and histopathologic evaluation of hidradenitis suppurativa treated with long‐pulsed Nd:YAG laser. 67th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, AAD San Francisco, CA United States. Conference Start: 20090306 Conference End: 20090310. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2009;60(3 Suppl 1):AB192. [EMBASE: 70142480]
-
- Mahmoud BH, Tierney E, Hexsel CL, Pui J, Ozog DM, Hamzavi IH. Prospective controlled clinical and histopathologic study of hidradenitis suppurativa treated with the long‐pulsed neodymium:yttrium‐aluminium‐garnet laser. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2010;62(4):637‐45. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Tierney E, Mahmoud BH, Hexsel C, Ozog D, Hamzavi I. Randomized control trial for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa with a neodymium‐doped yttrium aluminium garnet laser. Dermatologic Surgery 2009;35(8):1188‐98. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Morgan 1983 {published data only}
NCT00722800 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00722800. A Study to Examine the Safety and Efficacy of Drospirenone and Ethinyl Estradiol (YAZ) Versus Placebo In HS. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00722800 (accessed 2 April 2015).
Puri 2011 {published data only}
Soldin 2000 {published data only}
-
- Soldin MG, Tulley P, Kaplan H, Hudson DA, Grobbelaar AO. Chronic axillary hidradenitis‐‐the efficacy of wide excision and flap coverage. British Journal of Plastic Surgery 2000;53(5):434‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Xu 2011 {published data only}
-
- Xu LY, Wright DR, Mahmoud BH, Ozog DM, Mehregan DA, Hamzavi IH. Histopathologic study of hidradenitis suppurativa following long‐pulsed 1064‐nm Nd:YAG laser treatment. Archives of Dermatology 2011;147(1):21‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
EUCTR2006‐005405‐67 {published data only}
-
- EUCTR2006‐005405‐67. Study of the effectiveness and tolerance of L35 versus placebo in the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa (Verneuil 's Disease) [Etude de l'efficacité et de la tolérance du L35 versus placebo dans le traitement de l'hidradénite suppurée (Maladie de Verneuil)]. www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr‐search/search?query=2006‐005405‐67 (accessed 2 April 2015).
EUCTR2007‐000534‐39 {published data only}
-
- EUCTR2007‐000534‐39. Comparative randomised study on the effectiveness of the treatment of hidradenitis suppurative disease or verneuil by sub cutaneous injections of botulinum toxin versus placebo [Etude comparative randomisee intra‐individuelle de l'efficacite du traitement d'hidradenite suppuree ou maladie de verneuil par injections sous cutanee de toxine botulinique versus placebo]. www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr‐search/trial/2007‐000534‐39/FR (accessed 2 April 2015).
Servant 2002 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Servant JM, Couturaud B, Briand E. Algosteril range (calcium alginate rope/dressing/powder) versus tulle gras lumiere/vaseline (vaseline gauze) in the treatment of lesions due to Verneuil's disease. 4th Australian Wound Management Association Conference, Adelaide, South Australia. Adelaide, 2002.
References to ongoing studies
NCT01063270 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01063270. Trial Comparing Efficacy of Treatments for Hidradenitis Suppurativa. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01063270 (accessed 17 September 2014).
NCT01468207 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Jemec GB, Sundaram M, Pinsky B, Gu Y, Williams D, Bao Y. Adalimumab improves treatment satisfaction with medication (TS‐M) in patients with moderate to severe Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) in a 12‐week randomised controlled trial (PIONEER I). 44th Annual Meeting of the European Society for Dermatological Research Copenhagen Denmark. Conference Start: 20140910 Conference End: 20140913. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2014;134:S31. [EMBASE: 71606497]
-
- Kimball A, Zouboulis C, Armstrong A, Korman N, Crowley J, Lynde C, et al. Safety and efficacy of adalimumab in patients with moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa: Results from first 12 weeks of PIONEER I, a phase 3, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. 73rd Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology San Francisco, CA United States. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2015;72(5 Suppl 1):AB60. [EMBASE: 71895003]
-
- Kimball A, Zouboulis CC, Armstrong AW, Korman N, Crowley JJ, Lynde C, et al. Safety and efficacy of adalimumab in patients with moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa: results from first 12 weeks of PIONEER I, a phase 3, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. 44th Annual Meeting of the European Society for Dermatological Research Copenhagen Denmark. Conference Start: 20140910 Conference End: 20140913. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2014;134:S36. [EMBASE: 71606530]
-
- NCT01468207. Efficacy and Safety Study of Adalimumab in Treatment of Hidradenitis Suppurativa (PIONEER I). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01468207 (accessed 17 September 2014).
NCT01468233 {unpublished data only}
-
- Armstrong A, Pinsky B, Sundaram M, Shu L, Okun M, Bao Y. Adalimumab improves health‐related quality of life (HRQoL) in patients with moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa (HS): results from the first 12 weeks of PIONEER II. 73rd Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology San Francisco, CA United States. Conference Start: 20150320 Conference End: 20150324. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2015;72(5 Suppl 1):AB38. [EMBASE: 71894918]
-
- Jemec G, Gottlieb A, Forman S, Giamarellos‐Bourboulis E, Reguiai Z, Gu Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in patients with moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa: Results from PIONEER II, a phase 3, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. 73rd Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology San Francisco, CA United States. Conference Start: 20150320 Conference End: 20150324. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2015;72(5 Suppl 1):AB45. [EMBASE: 71894944]
-
- Jemec GBE, Sundaram M, Pinsky B, Shu L, Okun, M, Bao Y. Adalimumab improves treatment satisfaction with medication (TS‐M) in patients with moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) in a 12‐week randomized controlled trial (PIONEER II). Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2015;72(5 Suppl 1):AB39. [EMBASE: 71894919]
-
- Kimball AB, Pinsky B, Sundaram M, Geng Z, Okun M, Bao Y. Adalimumab is associated with reduced skin pain in patients with moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa (HS): Results from the first 12 weeks of PIONEER II. 73rd Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology San Francisco, CA United States. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2015;72(5 Suppl 1):AB39. [EMBASE: 71894920]
-
- NCT01468233. Efficacy and Safety Study of Adalimumab in the Treatment of Hidradenitis Suppurativa (PIONEER II). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01468233 (accessed 17 September 2014).
NCT01558375 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01558375. Anakinra in Hidradenitis Suppurativa. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01558375 (accessed 17 September 2014).
NCT01818167 {published data only}
-
- NCT01818167. An Investigation Into the Efficacy of Provodine Topical Cream as Compared to 10% Benzoyl Peroxide Wash for the Treatment of Hidradenitis Suppurativa. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01818167 (accessed 2 April 2015).
NCT01838499 {published data only}
-
- NCT01838499. Assessment of the Safety, Tolerability and Efficacy of MEDI8968 in Subjects With Moderate to Severe Hidradenitis Suppurativa. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01838499 (accessed 2 April 2015).
NCT02163746 {published data only}
-
- NCT02163746. Study to Compare Two Treatments for Axillary Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Carbon Dioxide Laser Versus Surgical Deroofing. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02163746 (accessed 2 April 2015).
NCT02421172 {published data only}
-
- NCT02421172. Efficacy, Safety, and Pharmacokinetics Study of CJM112 in Hidradenitis Suppurativa Patients. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02421172 (accessed 2 April 2015).
Additional references
Alhusayen 2012
-
- Alhusayen R, Shear NH. Pharmacologic interventions for hidradenitis suppurativa: what does the evidence say?. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology 2012;13(5):283‐91. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Basra 2008
-
- Basra MK, Fenech R, Gatt RM, Salek MS, Finlay AY. The Dermatology Life Quality Index 1994‐2007: a comprehensive review of validation data and clinical results. British Journal of Dermatology 2008;159(5):997‐1035. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Basra 2015
-
- Basra MK, Salek MS, Camilleri L, Sturkey R, Finlay AY. Determining the minimal clinically important difference and responsiveness of the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI): further data. Dermatology 2015;230(1):27‐33. [EMBASE: 2015703605] - PubMed
Blok 2013
-
- Blok JL, Hattem S, Jonkman MF, Horváth B. Systemic therapy with immunosuppressive agents and retinoids in hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review. British Journal of Dermatology 2013;168(2):243‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Egger 1997
Finlay 1994
-
- Finlay AY, Khan GK. Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) ‐ a simple practical measure for routine clinical use. Clinical & Experimental Dermatology 1994;19(3):210‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Finlay 2005
-
- Finlay AY. Current severe psoriasis and the Rule of Tens. British Journal of Dermatology 2005;152(5):861‐7. [EMBASE: 2005228623] - PubMed
Fitzsimmons 1985
-
- Fitzsimmons JS, Guilbert PR, Fitzsimmons EM. Evidence of genetic factors in hidradenitis suppurativa. British Journal of Dermatology 1985;113(1):1‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Harrison 1987
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org. The Cochrane Collaboration.
Hsiao 2010
-
- Hsiao JL, Antaya RJ, Berger T, Maurer T, Shinkai K, Leslie KS. Hidradenitis suppurativa and concomitant pyoderma gangrenosum: a case series and literature review. Archives of Dermatology 2010;146(11):1265‐70. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hurley 1989
-
- Hurley HJ. Axillary hyperhidrosis, apocrine bromhidrosis, hidradenitis suppurativa, and familial benign pemphigus: surgical approach. In: Roenigk RK, Roenigk HH editor(s). Dermatologic Surgery. New York: Marcel Dekker, 1989:729‐39.
Ingram 2012
Ingram 2014
Ioannidis 2005
-
- Ioannidis JP. Contradicted and initially stronger effects in highly cited clinical research. Journal of the American Medical Association 2005;294(2):218‐228. [EMBASE: 2005336655] - PubMed
Jemec 1996
-
- Jemec GB, Heidenheim M, Nielsen NH. The prevalence of hidradenitis suppurativa and its potential precursor lesions. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1996;35(2 Pt 1):191‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jemec 2012
-
- Jemec GB. Clinical practice. Hidradenitis suppurativa. New England Journal of Medicine 2012;366(2):158‐64. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kraft 2007
-
- Kraft JN, Searles GE. Hidradenitis suppurativa in 64 female patients: retrospective study comparing oral antibiotics and antiandrogen therapy. Journal of Cutaneous Medicine & Surgery 2007;11(4):125‐31. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kromann 2014
-
- Kromann CB, Deckers IE, Esmann S, Boer J, Prens EP, Jemec GB. Risk factors, clinical course and long‐term prognosis in hidradenitis suppurativa: a cross‐sectional study. British Journal of Dermatology 2014;171(4):819‐24. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kurek 2012
-
- Kurek A, Peters EM, Chanwangpong A, Sabat R, Sterry W, Schneider‐Burrus S. Profound disturbances of sexual health in patients with acne inversa. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2012;67(3):422‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Madan 2008
-
- Madan V, Hindle E, Hussain W, August PJ. Outcomes of treatment of nine cases of recalcitrant severe hidradenitis suppurativa with carbon dioxide laser. British Journal of Dermatology 2008;159(6):1309‐14. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mahmoud 2010
-
- Mahmoud BH, Tierney E, Hexsel CL, Pui J, Ozog DM, Hamzavi IH. Prospective controlled clinical and histopathologic study of hidradenitis suppurativa treated with the long‐pulsed neodymium:yttrium‐aluminium‐garnet laser. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2010;62:637‐45. - PubMed
Naldi 2006
-
- Naldi L. Epidemiology. In: Jemec GB, Revuz J, Leyden JJ editor(s). Hidradenitis Suppurativa. 1. Berlin: Springer, 2006:58‐64.
O'Rourke 1989
-
- O'Rourke K, Detsky AS. Meta‐analysis in medical research: strong encouragement for higher quality in individual research efforts. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1989;42(10):1021‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pink 2011
-
- Pink AE, Simpson MA, Brice GW, Smith CH, Desai N, Mortimer PS, et al. PSENEN and NCSTN mutations in familial hidradenitis suppurativa (acne inversa). Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2011;131(7):1568‐70. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rambhatla 2011
-
- Rambhatla PV, Lim HW, Hamzavi I. A Systematic Review of Treatments for Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Archives of Dermatology 2012;148(4):439‐46. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Revuz 2008
-
- Revuz JE, Canoui‐Poitrine F, Wolkenstein P, Viallette C, Gabison G, Pouget F, et al. Prevalence and factors associated with hidradenitis suppurativa: results from two case‐control studies. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2008;59(4):596‐601. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Revuz 2009
-
- Revuz J. Hidradenitis suppurativa. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology 2009;23(9):985‐98. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sartorius 2003
-
- Sartorius K, Lapins J, Emtestam L, Jemec GB. Suggestions for uniform outcome variables when reporting treatment effects in hidradenitis suppurativa. British Journal of Dermatology 2003;149(1):211‐3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sartorius 2009
-
- Sartorius K, Emtestam L, Jemec GB, Lapins J. Objective scoring of hidradenitis suppurativa reflecting the role of tobacco smoking and obesity. British Journal of Dermatology 2009;161(4):831‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sartorius 2010
-
- Sartorius K, Killasli H, Heilborn J, Jemec GB, Lapins J, Emtestam L. Interobserver variability of clinical scores in hidradenitis suppurativa is low. British Journal of Dermatology 2010;162(6):1261‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sartorius 2011
-
- Sartorius K, Killasli H, Oprica C, Sullivan A, Lapins J. Bacteriology of hidradenitis suppurativa exacerbations and deep tissue cultures obtained during carbon dioxide laser treatment. British Journal of Dermatology 2012;166(4):879‐83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Scheinfeld 2003
-
- Scheinfeld NS. A case of dissecting cellulitis and a review of the literature. Dermatology Online Journal 2003;9(1):8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Shavit 2014
van der Zee 2010
-
- Zee HH, Woude CJ, Florencia EF, Prens EP. Hidradenitis suppurativa and inflammatory bowel disease: are they associated? Results of a pilot study. British Journal of Dermatology 2010;162(1):195‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
van Rappard 2013
-
- Rappard DC, Limpens J, Mekkes JR. The off‐label treatment of severe hidradenitis suppurativa with TNF‐α inhibitors: a systematic review. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 2013;24(5):392‐404. [PUBMED: 22397574] - PubMed
von der Werth 2000 a
-
- Werth JM, Williams HC, Raeburn JA. The clinical genetics of hidradenitis suppurativa revisited. British Journal of Dermatology 2000;142(5):947‐53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
von der Werth 2000 b
-
- Werth JM, Williams HC. The natural history of hidradenitis suppurativa. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology 2000;14(5):389‐92. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
von Laffert 2011
-
- Laffert M, Stadie V, Wohlrab J, Marsch WC. Hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa: bilocated epithelial hyperplasia with very different sequelae. British Journal of Dermatology 2011;164(2):367‐71. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wang 2010
-
- Wang B, Yang W, Wen W, Sun J, Su B, Liu B, et al. Gamma‐secretase gene mutations in familial acne inversa. Science 2010;330(6007):1065. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

