Accuracy of abdominal ultrasound for the diagnosis of pneumoperitoneum in patients with acute abdominal pain: a pilot study
- PMID: 26443344
- PMCID: PMC4595408
- DOI: 10.1186/s13089-015-0032-6
Accuracy of abdominal ultrasound for the diagnosis of pneumoperitoneum in patients with acute abdominal pain: a pilot study
Abstract
Background: Pneumoperitoneum is a rare cause of abdominal pain characterized by a high mortality. Ultrasonography (US) can detect free intraperitoneal air; however, its accuracy remains unclear. The aims of this pilot study were to define the diagnostic performance and the reliability of abdominal US for the diagnosis of pneumoperitoneum.
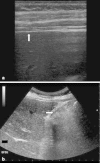
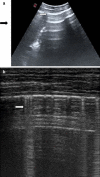
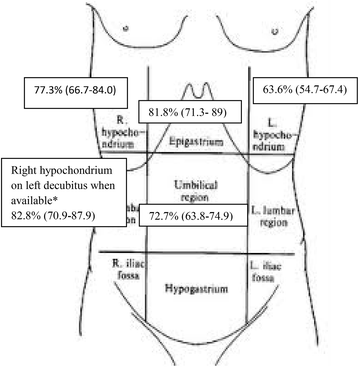
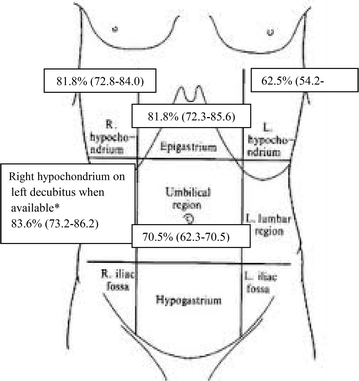
Methods: This was a prospective observational study. Four senior and two junior physicians were shown, in an unpaired randomized order, abdominal US videos from 11 patients with and 11 patients without pneumoperitoneum. Abdominal US videos were obtained from consecutive patients presenting to ED complaining abdominal pain with the diagnosis of pneumoperitoneum established by CT. Abdominal US was performed according to a standardized protocol that included the following scans: epigastrium, right and left hypochondrium, umbilical area and right hypochondrium with the patient lying on the left flank. We evaluated accuracy, intra- and inter-observer agreement of abdominal US when reviewed by senior physicians. Furthermore, we compared the accuracy of a "2 scan-fast exam" (epigastrium and right hypochondrium) vs the full US examination and the accuracy of physicians expert in US vs nonexpert ones. Finally, accuracy of US was compared with abdominal radiography in patients with available images.
Results: Considering senior revision, accuracy of abdominal US was 88.6 % (95 % CI 79.4-92.4 %) with a sensitivity of 95.5 % (95 % CI 86.3-99.2 %) and a specificity of 81.8 % (95 % CI 72.6-85.5 %). Inter- and intra-observer agreement (k) were 0.64 and 0.95, respectively. Accuracy of a "2 scan-fast exam" (87.5 %, 95 % CI 77.9-92.4 %) was similar to global exam. Sensitivity of abdominal radiography (72.2 %, 95 % CI 54.8-85.7 %) was lower than that of abdominal US, while specificity (92.5 %, 95 % CI 79.5-98.3 %) was higher. Accuracy (68.2 %, 95 % CI 51.4-80.9 %) of junior reviewers evaluating US was lower than senior reviewers.
Conclusions: Senior physicians can recognize US signs of pneumoperitoneum with a good accuracy and reliability; sensitivity of US could be superior to abdominal radiography and a 2 fast-scan exam seems as accurate as full abdominal examination. US could be a useful bedside screening test for pneumoperitoneum. Trial registry ClinicalTrials.gov; No.: NCT02004925; URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov.
Keywords: Abdominal pain; Abdominal radiography; Abdominal ultrasound; Hollow organ perforation diagnosis; Pneumoperitoneum diagnosis.
Figures
References
-
- Levine MS, Scheiner JD, Rubesin SE, Laufer I, Herlinger H (1991) Diagnosis of pneumoperitoneum on supine abdominal radiographs. Am J Roentgenol 156:340–345 - PubMed
-
- Shaffer HA., Jr Perforation and obstruction of the gastrointestinal tract. Assessment by conventional radiology. Radiol Clin North Am. 1992;30:405–426. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

