Meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy studies in mental health
- PMID: 26446042
- PMCID: PMC4680179
- DOI: 10.1136/eb-2015-102228
Meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy studies in mental health
Abstract
Objectives: To explain methods for data synthesis of evidence from diagnostic test accuracy (DTA) studies, and to illustrate different types of analyses that may be performed in a DTA systematic review.
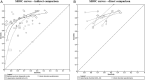
Methods: We described properties of meta-analytic methods for quantitative synthesis of evidence. We used a DTA review comparing the accuracy of three screening questionnaires for bipolar disorder to illustrate application of the methods for each type of analysis.
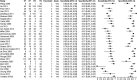
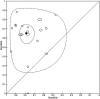
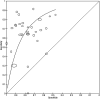
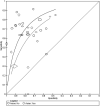
Results: The discriminatory ability of a test is commonly expressed in terms of sensitivity (proportion of those with the condition who test positive) and specificity (proportion of those without the condition who test negative). There is a trade-off between sensitivity and specificity, as an increasing threshold for defining test positivity will decrease sensitivity and increase specificity. Methods recommended for meta-analysis of DTA studies --such as the bivariate or hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic (HSROC) model --jointly summarise sensitivity and specificity while taking into account this threshold effect, as well as allowing for between study differences in test performance beyond what would be expected by chance. The bivariate model focuses on estimation of a summary sensitivity and specificity at a common threshold while the HSROC model focuses on the estimation of a summary curve from studies that have used different thresholds.
Conclusions: Meta-analyses of diagnostic accuracy studies can provide answers to important clinical questions. We hope this article will provide clinicians with sufficient understanding of the terminology and methods to aid interpretation of systematic reviews and facilitate better patient care.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Figures
References
-
- Dahabreh IJ, Chung M, Kitsios GD, et al. . Comprehensive overview of methods and reporting of meta-analyses of test accuracy. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, 2012. - PubMed
-
- Automated real-time nucleic acid amplification technology for rapid and simultaneous detection of tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance: Xpert MTB/RIF assay for the diagnosis of pulmonary and extrapulmonary TB in adults and children. Policy update. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
