Randomised controlled trial of weaning strategies for preterm infants on nasal continuous positive airway pressure
- PMID: 26446072
- PMCID: PMC4597764
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-015-0462-0
Randomised controlled trial of weaning strategies for preterm infants on nasal continuous positive airway pressure
Abstract
Background: The optimal strategy for weaning very preterm infants from nasal continuous positive airway pressure (NCPAP) is unclear. Reported strategies include weaning NCPAP to a predefined pressure then trialling stopping completely (abrupt wean); alternate periods of increased time off NCPAP whilst reducing time on until the infant is completely weaned (gradual wean); and using high flow nasal cannula (HFNC) to assist the weaning process. The aim of this study was to determine the optimal weaning from NCPAP strategy for very preterm infants.
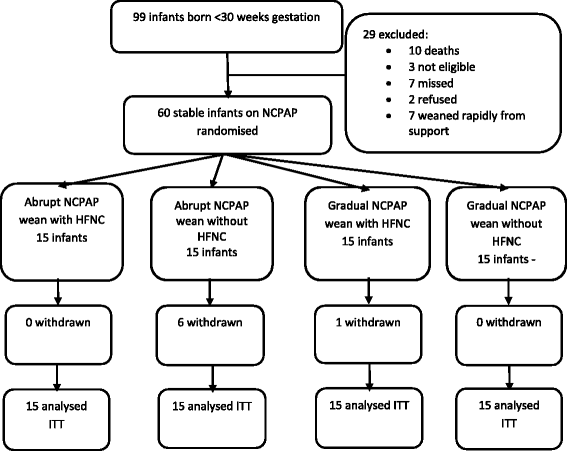
Methods: A pilot single centre, factorial design, 4-arm randomised controlled trial. Sixty infants born <30 weeks gestation meeting stability criteria on NCPAP were randomly allocated to one of four groups. Group 1: abrupt wean with HFNC; Group 2: abrupt wean without HFNC; Group 3: gradual wean with HFNC; Group 4: gradual wean without HFNC. The primary outcomes were duration of respiratory support, chronic lung disease, length of hospital stay and time to full suck feeds.
Results: The primary outcome measures were not significantly different between groups. Group 1 had a significant reduction in duration of NCPAP (group 1: median 1 day; group 2: 24 days; group 3: 15 days; group 4: 24 days; p = 0.002) and earlier corrected gestational age off NCPAP. There was a significant difference in rate of parental withdrawal from the study, with group 2 having the highest rate. Group 3 had a significantly increased duration on HFNC compared to group 1.
Conclusions: Use of high flow nasal cannula may be effective at weaning infants from NCPAP but did not reduce duration of respiratory support or time to full suck feeds. Abrupt wean without the use of HFNC was associated with an increased rate of withdrawal by parent request.
Trial registration: This study is registered at the Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry ( www.anzctr.org.au/). (Registration Number = ACTRN12610001003066).
Figures
References
-
- Ho JJ, Subramaniam P, Henderson-Smart DJ, Davis PG. Continuous distending pressure for respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;2:CD002271. - PubMed
-
- Rojas-Reyes MX, Morley CJ, Soll R. Prophylactic versus selective use of surfactant in preventing morbidity and mortality in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;3:CD000510. - PubMed
-
- Davis PG, Henderson-Smart DJ. Nasal continuous positive airways pressure immediately after extubation for preventing morbidity in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;2:CD000143. - PubMed
-
- Jardine LA, Inglis GD, Davies MW. Strategies for the withdrawal of nasal continuous positive airway pressure (NCPAP) in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;2:CD006979. - PubMed
-
- Singh SD, Clarke P, Bowe L, Glover K, Pasquill A, Robinson MJ, Smith JE. Nasal CPAP weaning of VLBW infants: Is decreasing CPAP pressure or increasing time off the better strategy? Results of a randomised controlled trial. Early Hum Dev. 2006;9:130–1.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical