Interventions for fatigue in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 26447539
- PMCID: PMC9240814
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010925.pub2
Interventions for fatigue in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Background: Factors contributing to subjective fatigue in people with idiopathic Parkinson's disease (PD) are not well known. This makes it difficult to manage fatigue effectively in PD.
Objectives: To evaluate the effects of pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions, compared to an inactive control intervention, on subjective fatigue in people with PD.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library); MEDLINE (via PubMed); Ovid EMBASE; EBSCO CINAHL; Ovid PsycINFO; PEDro; and the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform Search Portal up to April 2015. References of included studies and identified review articles were screened for additional studies. There were no restrictions based on language, date of publication or study setting.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) that report on subjective fatigue in people with PD.
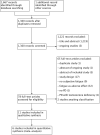
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently performed study selection, data collection and risk of bias assessments.
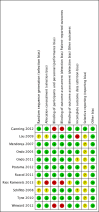
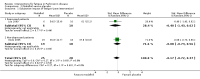
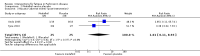
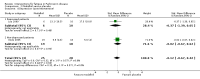
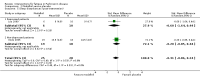
Main results: Eleven studies were eligible for this systematic review, with a total of 1817 people. Three studies included only people who experienced clinically relevant fatigue (Fatigue Severity Scale score ≥ 4 out of 7 or Multidimensional Fatigue Inventory total score > 48 out of 100), whereas all other studies did not select participants on the basis of experienced fatigue. Nine studies investigated the effects of medication (i.e. levodopa-carbidopa, memantine, rasagiline, caffeine, methylphenidate, modafinil or doxepin) on subjective fatigue. All studies were placebo controlled. There was insufficient evidence to determine the effect of doxepin on the impact of fatigue on activities in daily life (ADL) or fatigue severity (one study, N = 12, standardised mean difference (SMD) = -1.50, 95% confidence interval (CI) -2.84 to -0.15; low quality evidence). We found high quality evidence that rasagiline reduced or slowed down the progression of physical aspects of fatigue (one study, N = 1176, SMD = -0.27, 95% CI -0.39 to -0.16, I(2) = 0%). None of the other pharmacological interventions affected subjective fatigue in PD. With regard to adverse effects, only levodopa-carbidopa showed an increase for the risk of nausea (one study, N = 361, risk ratio (RR) = 1.85, 95% CI 1.05 to 3.27; high quality evidence). Two studies investigated the effect of exercise on fatigue compared with usual care. We found low quality evidence for the effect of exercise on reducing the impact of fatigue on ADL or fatigue severity (two studies, N = 57, SMD = -0.45, 95% CI -1.21 to 0.32, I(2) = 44%).
Authors' conclusions: Based on the current evidence, no clear recommendations for the treatment of subjective fatigue in PD can be provided. Doxepin may reduce the impact of fatigue on ADL and fatigue severity; however, this finding has to be confirmed in high quality studies. Rasagiline may be effective in reducing levels of physical fatigue in PD. No evidence was found for the effectiveness of levodopa-carbidopa, memantine, caffeine, methylphenidate, modafinil or exercise. Studies are needed to investigate the effect of exercise intensity on exercise capacity and subjective fatigue. Future studies should focus on interventions that address the maladaptive behavioural or cognitive aspects of fatigue in people with PD. Characteristics, such as severity and nature of perceived fatigue and underlying mood disorders should be considered to identify responders and non-responders when studying interventions for fatigue. The development of a core-set of self-report fatigue questionnaires with established responsiveness and known minimal important difference values will facilitate the interpretation of change in fatigue scores.
Conflict of interest statement
Roy G Elbers: none known.
John Verhoef: none known.
Erwin EH van Wegen: none known.
Henk W Berendse: none known.
Gert Kwakkel: none known.
Figures


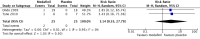
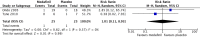

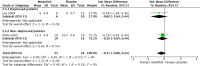
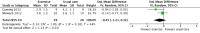
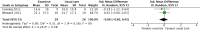




Comment in
-
Treatment of Fatigue in Parkinson Disease.JAMA. 2016 Jun 7;315(21):2340-1. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.5260. JAMA. 2016. PMID: 27272586
References
References to studies included in this review
Canning 2012 {published data only}
-
- Canning C, Allen N, Dean C, Goh L, Fung V. Home‐based treadmill training for individuals with Parkinson's disease: a randomized controlled pilot trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2012;26:817‐26. - PubMed
Lou 2009 {published data only}
-
- Lou J, Dimitrova D, Park B, Johnson S, Eaton R, Arnold G, et al. Using modafinil to treat fatigue in Parkinson disease: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled pilot study. Clinical Neuropharmacology 2009;32:305‐10. - PubMed
Mendonça 2007 {published data only}
-
- Mendonça D, Menezes K, Jog M. Methylphenidate improves fatigue scores in Parkinson's disease: a randomized controlled trial. Movement Disorders 2007;22:2070‐6. - PubMed
Ondo 2005 {published data only}
Ondo 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ondo W, Shinawi L, Davidson A, Lai D. Memantine for non‐motor features of Parkinson's disease: a double‐blind placebo controlled exploratory pilot trial. Parkinsonism and Related Disorders 2011;17:156‐9. - PubMed
Postuma 2012 {published data only}
Rascol 2011 {published data only}
-
- Rascol O, Fitzer‐Attas C, Hauser R, Jankovic J, Lang A, Langston J, et al. A double‐blind, delayed‐start trial of rasagiline in Parkinson's disease (the ADAGIO study): prespecified and post‐hoc analysis of the need for additional therapies, change in UPDRS scores, and non‐motor outcomes. Lancet Neurology 2011;10:415‐23. - PubMed
Rios Romenets 2013 {published data only}
-
- Rios Romenets S, Creti L, Fichten C, Bailes S, Libman E, Pelletier A, et al. Doxepin and cognitive behavioural therapy for insomnia in patients with Parkinson’s disease – a randomized study. Parkinsonism and Related Disorders 2013;19:670‐5. - PubMed
Schifitto 2008 {published data only}
Tyne 2010 {published data only}
-
- Tyne H, Taylor J, Baker G, Steiger M. Modafinil for Parkinson's disease fatigue. Journal of Neurology 2010;257:452‐6. - PubMed
Winward 2012 {published data only}
-
- Winward C, Sackley C, Meek C, Izadi H, Barker K, Wade D, et al. Weekly exercise does not improve fatigue levels in Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2012;27:143‐6. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abe 2001 {published data only}
Barone 2010 {published data only}
-
- Barone P, Poewe W, Albrecht S, Debieuvre C, Massey D, Rascol O, et al. Pramipexole for the treatment of depressive symptoms in patients with Parkinson's disease: a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Lancet Neurology 2010;9:573‐80. - PubMed
Barone 2011 {published data only}
-
- Barone P. Treatment of depressive symptoms in Parkinson's disease. European Journal of Neurology 2011;18:11‐5. - PubMed
Berman 2011 {published data only}
Blindauer 2003 {published data only}
-
- Blindauer K, Shoulson I, Kieburtz K, McDermott M, Gardiner I, Kamp C, et al. A controlled trial of rotigotine monotherapy in early Parkinson's disease. Archives of Neurology 2003;60:1721‐8. - PubMed
Borgohain 2014 {published data only}
-
- Borgohain R, Szasz J, Stanzione P, Meshram C, Bhatt M, Chirillineau D, et al. Two‐year, randomized, controlled study of safinamide as add‐on to levodopa in mid to late Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2014;29:1273‐80. - PubMed
Bronzova 2010 {published data only}
-
- Bronzova J, Sampaio C, Hauser R, Lang A, Rascol O, Theeuwes A, et al. Double‐blind study of pardoprunox, a new partial dopamine agonist, in early Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2010;25:738‐46. - PubMed
Brooks 2003 {published data only}
Chaudhuri 2013 {published data only}
-
- Chaudhuri K, Martínez‐Martín P, Antonini A, Brown R, Friedman J, Onofrj M, et al. Rotigotine and specific non‐motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: post hoc analysis of RECOVER. Parkinsonism and Related Disorders 2013;19:660‐5. - PubMed
Chwieduk 2010 {published data only}
-
- Chwieduk C, Curran M. Pramipexole extended release in Parkinson's disease. CNS Drugs 2010;24:327‐36. - PubMed
Conradsson 2013 {published data only}
-
- Conradsson D, Lofgren N, Hagstromer M, Stahle A, Franzen E. A highly challenging, progressive and specific balance training program in elderly with Parkinson’s disease: theoretical framework and feasibility. European Journal of Neurology 2013;19:S571.
Cugusi 2014 {published data only}
-
- Cugusi L, Solla P, Zedda F, Loi M, Serpe R, Cannas A, et al. Effects of an adapted physical activity program on motor and non‐motor functions and quality of life in patients with Parkinson's disease. Neurorehabilitation 2014;35:789‐94. - PubMed
Dashtipour 2015 {published data only}
Datieva 2013 {published data only}
-
- Datieva V, Rosinskaia A, Levin O. The use of melatonin in the treatment of chronic fatigue sundrome and circadian rhythm disorders in Parkinson’s disease. Zhurnal Nevrologii I Psikhiatrii Imeni SS Korsokova 2013;113:77‐81. - PubMed
Deuschl 2007 {published data only}
-
- Deuschl G, Vaitkus A, Fox G, Roscher T, Schremmer D, Gordin A. Efficacy and tolerability of entacapone versus cabergoline in Parkinsonian patients suffering from wearing‐off. Movement Disorders 2007;22:1550‐5. - PubMed
Devos 2007 {published data only}
Dobato 1994 {published data only}
-
- Dobato J, Pérez‐Gilabert Y, Andrés C, Muñoz‐Blanco J, Mateo D, Giménez‐Roldán S. Effect of amantadine on fatigue in Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [Efecto del amantadine en la fatiga de la enfermedad de Parkinson, la esclerósis múltiple y la esclerósis lateral amiotrófica]. NeurologÌa 1994;9:460.
Dowling 2005 {published data only}
-
- Dowling G, Mastick J, Colling E, Carter J, Singer C, Aminoff M. Melatonin for sleep disturbances in Parkinson's disease. Sleep Medicine 2005;6:459‐66. - PubMed
Drijgers 2012 {published data only}
-
- Drijgers R, Verhey F, Tissingh G, Domburg P, Aalten P, Leentjens A. The role of the dopaminergic system in mood, motivation and cognition in Parkinson's disease: a double blind randomized placebo controlled experimental challenge with pramipexole and methylphenidate. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2012;320:121‐6. - PubMed
Fernandez 2010 {published data only}
-
- Fernandez H, Greeley D, Zweig R, Wojcieszek J, Mori A, Sussman N. Istradefylline as monotherapy for Parkinson disease: results of the 6002‐US‐051 trial. Parkinsonism and Related Disorders 2010;16:16‐20. - PubMed
Genç 2012 {published data only}
-
- Genç A, Dönmez Çolakoğlu B, Kara B, Çakmur R. Evaluation of the effects of home‐based deep breathing exercises in Parkinson's disease patients. Archives of Neuropsychiatry 2012;49:59‐62.
Ghahari 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ghahari S, Packer T, Passmore A. Effectiveness of an online fatigue self‐management programme for people with chronic neurological conditions: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2010;24:727‐44. - PubMed
Grosset 2005 {published data only}
-
- Grosset K, Grosset D, Lees A. Trial of subtherapeutic pergolide in de novo Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2005;20:363‐6. - PubMed
Hauser 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hauser R, Salin L, Juhel N, Konyago V. Randomized trial of the triple monoamine reuptake inhibitor NS 2330 (tesofensine) in early Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2007;22:359‐65. - PubMed
Hauser 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hauser R, Lyons K, McClain T, Carter S, Perlmutter D. Randomized, double‐blind, pilot evaluation of intravenous glutathione in Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2009;24:979‐83. - PubMed
Hauser 2010 {published data only}
-
- Hauser R, Schapira A, Rascol O, Barone P, Mizuno Y, Salin L, et al. Randomized, double‐blind, multicenter evaluation of pramipexole extended release once daily in early Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2010;25:2542‐9. - PubMed
Heikkinen 2001 {published data only}
-
- Heikkinen H, Nutt J, LeWitt P, Koller W, Gordin A. The effects of different repeated doses of entacapone on the pharmacokinetics of l‐dopa and on the clinical response to l‐dopa in Parkinson's disease. Clinical Neuropharmacology 2001;24:150‐7. - PubMed
Jang 2014 {published data only}
-
- Jang W, Park J, Shin K, Kim J, Kim J, Youn J, et al. Safety and efficacy of recombinant human erythropoietin treatment of non‐motor symptoms in Parkinson's disease. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2014;337:47‐54. - PubMed
Jankovic 2007 {published data only}
-
- Jankovic J, Watts R, Martin W, Boroojerdi B. Transdermal rotigotine: double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial in Parkinson disease. Archives of Neurology 2007;64:676‐82. - PubMed
Kieburtz 1996 {published data only}
-
- Kieburtz K, McDermott M, Shoulson I, Fahn S, Brin M, Goetz C, et al. Effect of lazabemide on the progression of disability in early Parkinson's disease. Annals of Neurology 1996;40:99‐107. - PubMed
Kieburtz 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kieburtz K, The Parkinson Study Group PramiBID Investigators. Twice‐daily, low dose Pramipexole in early Parkinson's disease:a randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Movement Disorders 2011;26:37‐44. - PubMed
Leentjens 2006 {published data only}
-
- Leentjens A, Scholtissen B, Vreeling F, Verhey F. The serotonergic hypothesis for depression in Parkinson's disease: an experimental approach. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006;31:1009‐15. - PubMed
Leroi 2004 {published data only}
-
- Leroi I, Brandt J, Reich S, Lyketsos C, Grill S, Thompson R, et al. Randomized placebo‐controlled trial of donepezil in cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2004;19:1‐8. - PubMed
Lim 2013 {published data only}
-
- Lim T, Kluger B, Rodriguez R, Palacio R, Guirati Y, Nutter B, et al. Rasagiline for the symptomatic treatment of fatigue in Parkinson’s disease: a 3‐center, placebo‐controlled, pilot study (the REST trial). Movement Disorders 2013;28:S165. - PubMed
Lou 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lou J, Kearns G, Benice T, Oken B, Sexton G, Nutt J. Levodopa improves physical fatigue in Parkinson's diseae: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, crossover study. Movement Disorders 2003;18:1108‐14. - PubMed
Meek 2010 {published data only}
-
- Meek C, Sackley C, Clarke C, Soundy A, Winward C, Esser P, et al. Long‐term individual fitness enablement (LIFE) for Parkinson's disease: a feasibility study. Movement Disorders 2010;25:S713.
Menza 2009 {published data only}
Möller 2005 {published data only}
-
- Möller J, Oertel W, Köster J, Pezzoli G, Provinciali L. Long‐term efficacy and safety of pramipexole in advanced Parkinson's disease: results from a European multicenter trial. Movement Disorders 2005;20:602‐10. - PubMed
Morita 2011 {published data only}
-
- Morita A, Okuma Y, Kamei S, Yoshii F, Yamamoto T, Hashimoto S, et al. Pramipexole reduces the prevalence of fatigue in patients with Parkinson's disease. Internal Medicine 2011;50:2163‐8. - PubMed
Nutt 2007 {published data only}
-
- Nutt J, Carter J, Carlson N. Effects of methylphenidate on response to oral levodopa. Archives of Neurology 2007;64:319‐23. - PubMed
Okun 2006 {published data only}
-
- Okun M, Fernandez H, Rodriguez R, Romrell J, Suelter M, Munson S, et al. Testosterone therapy in men with Parkinson disease. Archives of Neurology 2006;63:729‐35. - PubMed
Olanow 2004 {published data only}
-
- Olanow C, Kieburtz K, Stern M, Watts R, Langston W, Guarnieri M, et al. Double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of entacapone in levodopa‐treated patients with stable Parkinson disease. Archives of Neurology 2004;61:1563‐8. - PubMed
Ondo 2008 {published data only}
-
- Ondo W, Perkins T, Swick T, Hull K, Jimenez J, Garris T, et al. Sodium oxybate for excessive daytime sleepiness in Parkinson disease. Archives of Neurology 2008;65:1337‐40. - PubMed
Oved 2006 {published data only}
-
- Oved D, Ziv I, Treves T, Paleacu D, Melamed E, Djaldetti R. Effect of dopamine agonist on fatigue and somnolence in Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2006;21:1257‐61. - PubMed
Pinter 1999 {published data only}
-
- Pinter M, Pogarell O, Oertel W. Efficacy, safety, and tolerance of the non‐ergoline dopamine agonist pramipexole in the treatment of advanced Parkinson's disease: a double blind, placebo controlled, randomised, multicentre study. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 1999;66:436‐41. - PMC - PubMed
Pogarell 2002 {published data only}
-
- Pogarell O, Gasser T, Hilten J, Spieker S, Pollentier S, Meier D, et al. Pramipexole in patients with Parkinson's disease and marked drug resistant tremor: a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled multicentre study. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 2002;72:713‐20. - PMC - PubMed
Pourcher 2012 {published data only}
-
- Pourcher E, Fernandez H, Stacy M, Mori A, Ballerini R, Chaikin P. Istradefylline for Parkinson's disease patients experiencing motor fluctuations: results of the KW‐6002‐US‐018 study. Parkinsonism and Related Disorders 2012;18:178‐84. - PubMed
Richard 2012 {published data only}
Rios Romenets 2015 {published data only}
-
- Rios Romenets S, Anang J, Fereshtehnejad S, Pelletier A, Postuma R. Tango for treatment of motor and non‐motor manifestations in Parkinson's disease: a randomized control study. Complementary Therapies in Medicine 2015;23:175‐84. - PubMed
Sampaio 2011 {published data only}
-
- Sampaio C, Bronzova J, Hauser R, Lang A, Rascol O, Witte S, et al. Pardoprunox in early Parkinson's disease: results from 2 large, randomized double‐blind trials. Movement Disorders 2011;26:1464‐76. - PubMed
Schapira 2013 {published data only}
Sethi 1998 {published data only}
-
- Sethi K, O'Brien C, Hammerstad J, Adler C, Davis T, Taylor R, et al. Ropinirole for the treatment of early Parkinson disease: a 12‐month experience. Archives of Neurology 1998;55:1211‐6. - PubMed
Shoulson 2002 {published data only}
-
- Shoulson I, Oakes D, Fahn S, Lang A, Langston W, LeWitt P, et al. Impact of sustained deprenyl (selegiline) in levodopa‐treated Parkinson's disease: a randomized placebo‐controlled extension of the deprenyl and tocopherol antioxidative therapy of Parkinsonism trial. Annals of Neurology 2002;51:604‐12. - PubMed
Singer 2007 {published data only}
-
- Singer C, Lamb J, Ellis A, Layton G. A comparison of sumanirole versus placebo or ropinirole for the treatment of patients with early Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2007;22:476‐82. - PubMed
Stocchi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Stocchi F. Benefits of treatment with rasagiline in fatigue symptoms in patients with early Parkinson's disease. European Journal of Neurology 2009;16:S525. - PubMed
Stocchi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Stocchi F. Treatment with rasagiline provides benefits in the symptoms of fatigue in patients with early Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2010;25:S676.
Stocchi 2013 {published data only}
-
- Stocchi F, Rascol O, Destee A, Hattori N, Hauser R, Lang A, et al. AFQ056 in Parkinson patients with levodopa‐induced dyskinesia: 13‐week, randomized, dose‐finding study. Movement Disorders 2013;28:1838‐46. - PubMed
Stocchi 2014 {published data only}
-
- Stocchi F, The ADAGIO Investigators. Benefits of treatment with rasagiline for fatigue symptoms in patients with early Parkinson’s disease. European Journal of Neurology 2014;21:357‐60. - PubMed
Sturkenboom 2014 {published data only}
-
- Sturkenboom I, Graff M, Hendriks J, Veenhuizen Y, Munneke M, Bloem B, et al. Efficacy of occupational therapy for patients with Parkinson's disease: a randomised controlled trial. The Lancet Neurology 2014;13:557‐66. - PubMed
Todorova 2013 {published data only}
-
- Todorova A, Martinez‐Martin P, Martin A, Rizos A, Reddy P, Chaudhuri K. Datyime apomorphine infusion combined with transdermal rotigotine patch therapy is tolerated at 2 years: a 24‐h treatment option in Parkinson's disease. Basal Ganglia 2013;3:127‐30.
Trenkwalder 2010 {published data only}
-
- Trenkwalder C, Zucconi M, Tolosa E, Surmann E, Whitesides J, Boroojerdi B, et al. Effect of rotigotine on sleep outcomes in Parkinson's disease: recover study. Journal of Sleep Research 2010;19:S23‐S4.
Uc 2014 {published data only}
Watts 2007 {published data only}
-
- Watts R, Jankovic J, Waters C, Rajput A, Boroojerdi B, Rao J. Randomized, blind, controlled trial of transdermal rotigotine in early Parkinson disease. Neurology 2007;68:272‐7. - PubMed
Zhang 2013a {published data only}
-
- Zhang L, Zhang Z, Chen Y, Qin X, Zhou H, Zhang C, et al. Efficacy and safety of rasagiline as an adjunct to levodopa treatment in Chinese patients with Parkinson’s disease: a randomized, double‐blind, parallel‐controlled, multi‐centre trial. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2013;16:1529‐37. - PubMed
Zhang 2013b {published data only}
-
- Zhang Z, Wang J, Zhang X, Chen S, Wang Z, Zhang B, et al. The efficacy and safety of ropinirole prolonged release tablets as adjunctive therapy in Chinese subjects with advanced Parkinson’s disease: a multicenter, double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled study. Parkinsonism and Related Disorders 2013;19:1022‐6. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Pahwa 2015 {published data only}
Smith 2015 {published data only}
-
- Smith K, Eyal E, Weintraub D. Combined rasagiline and antidepressant use in Parkinson disease in the ADAGIO study. JAMA Neurology 2015;72:88‐95. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
EUCTR2007‐002195‐34‐FR {published data only}
-
- Evaluation of the effect of 6 months treatment with DC158AM on fatigue in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Multicenter, randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study in parallel groups.. Ongoing study February 2008 (first enrollment)..
NCT01168596 {published data only}
-
- Rasagiline for the symptomatic treatment of fatigue in Parkinson's disease (REST).. Ongoing study December 2009 (first enrollment)..
NCT01360229 {published data only}
-
- Acupuncture for fatigue in Parkinson's disease.. Ongoing study August 2010 (first enrollment)..
Additional references
Alves 2004
-
- Alves G, Wentzel‐Larsen T, Larsen J. Is fatigue an independent and persistent symptom in patients with Parkinson's disease?. Neurology 2004;63:1908‐11. - PubMed
APA 2013
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th Edition. Arlington: American Psychiatric Association, 2013.
Chaudhuri 2004
-
- Chaudhuri A, Behan P. Fatigue in neurological disorders. Lancet 2004;363:978‐88. - PubMed
Cohen 1988
-
- Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis in the Behavioral Sciences. 2nd edition. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc., 1988.
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Elbers 2012a
Elbers 2012b
-
- Elbers R, Wegen E, Verhoef J, Kwakkel G. Reliability and structural validity of the multidimensional fatigue inventory in patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism and Related Disorders 2012;18:532‐6. - PubMed
Fox 2011
-
- Fox S, Katzenschlager R, Lim S, Ravina B, Seppi K, Coelho M, et al. The Movement Discorder Society evidence‐based medicine review update: treatments for the motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2011;26:S2‐S41. - PubMed
Franssen 2014
-
- Franssen M, Winward C, Collet J, Wade D, Dawes H. Interventions for fatigue in Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Movement Disorders 2014;29:1675‐8. - PubMed
Friedman 2007
-
- Friedman J, Brown R, Comella C, Garber C, Krupp L, Lou J, et al. Fatigue in Parkinson's disease: a review. Movement Disorders 2007;22:297‐308. - PubMed
Friedman 2010
-
- Friedman J, Alves G, Hagell P, Marinus J, Marsh L, Martínez‐Martín P, et al. Fatigue rating scales critique and recommendations by the Movement Disorders Society Task Force on rating scales for Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders 2010;25:805‐22. - PubMed
Friedman 2011
-
- Friedman J, Abrantes A, Sweet L. Fatigue in Parkinson's disease. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 2011;12:1999‐2007. - PubMed
Frisina 2008
-
- Frisina P, Tenenbaum H, Borod J. The effects of antidepressants in Parkinson’s disease: a meta‐analysis. International Journal of Neuroscience 2008;118:667‐82. - PubMed
Guyatt 2011
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman A, Vist G, Kunz R, Brozek J, Alonson‐Coello P, et al. GRADE guidelines: 4. Rating the quality of evidence ‐ study limitations (risk of bias). Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64:407‐15. - PubMed
Havlikova 2008
-
- Havlikova E, Rosenberger J, NagyoveI, Middel B, Dubayova T, Gdovinova Z, et al. Impact of fatigue on quality of life in patients with Parkinson's disease. European Journal of Neurology 2008;15:475‐80. - PubMed
Herlofson 2002
-
- Herlofson K, Larsen J. Measuring fatigue in patients with Parkinson's disease—the fatigue severity scale. European Journal of Neurology 2002;9:595‐600. - PubMed
Herlofson 2003
-
- Herlofson K, Larsen J. The influence of fatigue on health‐related quality of life in patients with Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 2003;107:1‐6. - PubMed
Herlofson 2012
-
- Herlofson K, Ongre S, Enger L, Tysnes, O, Larsen, J. Fatigue in early Parkinson's disease. Minor inconvenience or major distress?. European Journal of Neurology 2012;19:963‐8. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins J, Altman D, Sterne J (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins J, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Johnston 2010
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins J, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Lou 2001
-
- Lou J, Kearns G, Oken B, Sexton G, Nutt J. Exacerbated physical fatigue and mental fatigue in Parkinson’s disease. Movement Disorders 2001;16:190‐6. - PubMed
Martínez‐Martín 2006
-
- Martínez‐Martín P, Catalan M, Benito‐León, Ortega Moreno A, Zamarbide I, Cubo E, et al. Impact of fatigue in Parkinson's disease: the fatigue impact scale for daily use (D‐FIS). Quality of Life Research 2006;15:597‐606. - PubMed
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann H, Oxman A, Vist G, Higgins J, Deeks J, Glasziou P, Guyatt G. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins J, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

