The axon guidance molecule semaphorin 3F is a negative regulator of tumor progression and proliferation in ileal neuroendocrine tumors
- PMID: 26447612
- PMCID: PMC4742207
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5481
The axon guidance molecule semaphorin 3F is a negative regulator of tumor progression and proliferation in ileal neuroendocrine tumors
Abstract
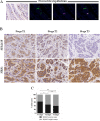
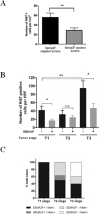
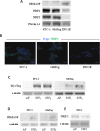
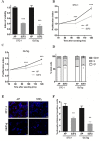
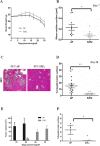
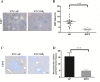
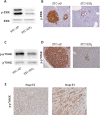
Gastro-intestinal neuroendocrine tumors (GI-NETs) are rare neoplasms, frequently metastatic, raising difficult clinical and therapeutic challenges due to a poor knowledge of their biology. As neuroendocrine cells express both epithelial and neural cell markers, we studied the possible involvement in GI-NETs of axon guidance molecules, which have been shown to decrease tumor cell proliferation and metastatic dissemination in several tumor types. We focused on the role of Semaphorin 3F (SEMA3F) in ileal NETs, one of the most frequent subtypes of GI-NETs.SEMA3F expression was detected in normal neuroendocrine cells but was lost in most of human primary tumors and all their metastases. SEMA3F loss of expression was associated with promoter gene methylation. After increasing endogenous SEMA3F levels through stable transfection, enteroendocrine cell lines STC-1 and GluTag showed a reduced proliferation rate in vitro. In two different xenograft mouse models, SEMA3F-overexpressing cells exhibited a reduced ability to form tumors and a hampered liver dissemination potential in vivo. This resulted, at least in part, from the inhibition of mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways.This study demonstrates an anti-tumoral role of SEMA3F in ileal NETs. We thus suggest that SEMA3F and/or its cellular signaling pathway could represent a target for ileal NET therapy.
Keywords: proliferation; semaphorin; small intestine neuroendocrine tumor; tumor progression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yao JC, Hassan M, Phan A, Dagohoy C, Leary C, Mares JE, Abdalla EK, Fleming JB, Vauthey J-N, Rashid A, Evans DB. One hundred years after “carcinoid”: epidemiology of and prognostic factors for neuroendocrine tumors in 35,825 cases in the United States. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3063–3072. - PubMed
-
- Cohen T, Gluzman-Poltorak Z, Brodzky A, Meytal V, Sabo E, Misselevich I, Hassoun M, Boss JH, Resnick M, Shneyvas D, Eldar S, Neufeld G. Neuroendocrine cells along the digestive tract express neuropilin-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;284:395–403. - PubMed
-
- Yang YHC, Szabat M, Bragagnini C, Kott K, Helgason CD, Hoffman BG, Johnson JD. Paracrine signalling loops in adult human and mouse pancreatic islets: netrins modulate beta cell apoptosis signalling via dependence receptors. Diabetologia. 2011;54:828–842. - PubMed
-
- Chédotal A, Kerjan G, Moreau-Fauvarque C. The brain within the tumor: new roles for axon guidance molecules in cancers. Cell Death Differ. 2005;12:1044–1056. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

