Somatostatin Receptor SSTR-2a Expression Is a Stronger Predictor for Survival Than Ki-67 in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
- PMID: 26447992
- PMCID: PMC4616753
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001281
Somatostatin Receptor SSTR-2a Expression Is a Stronger Predictor for Survival Than Ki-67 in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
Abstract
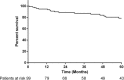
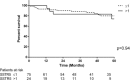
Somatostatin receptors (SSTR) are commonly expressed by neuroendocrine tumors. Expression of SSTR-2a and SSTR-5 may impact symptomatic management; however, the impact on survival is unclear. The aim of this study is to correlate SSTR-2a and SSTR-5 expression in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs) with survival. This study is designed to determine the prognostic significance of somatostatin receptors SSTR-2a and SSTR-5 in PNETs. This retrospective cohort study included cases of resected PNETs between 1992 and 2014. Clinical data, histopathology, expression of SSTR and Ki-67 by immunohistochemistry, and long-term survival were analyzed. A total of 99 cases were included in this study. The mean age was 57.8 years (18-87 years) and median tumor size was 25 mm (range 8-160 mm). SSTR-2a and SSTR-5 expression was scored as negative (n = 19, 19.2%; n = 75, 75.8%, respectively) and positive (n = 80, 80.1%; n = 24, 24.2%). The median follow-up was 49 months. SSTR-2a expression was associated with improved overall survival, with cumulative survival rates at 1, 3, and 5 years being 97.5%, 91.5%, and 82.9%, respectively. Univariate analysis demonstrated better survival in SSTR-2a positive patients (log rank P = 0.04). SSTR-5 expression was not associated with survival outcomes (log rank P = 0.94). Multivariate analysis showed that positive SSTR-2a expression is a stronger prognostic indicator for overall survival [Hazard Ratio (HR): 0.2, 95% Confidence interval (CI): 0.1-0.8] compared to high Ki-67 (HR: 0.8, 95% CI: 0.1-5.7). Expression of SSTR-2a is an independent positive prognostic factor for survival in PNETs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Fraenkel M, Kim MK, Faggiano A, et al. Epidemiology of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2012; 26:691–703. - PubMed
-
- Fazio N, Cinieri S, Lorizzo K, et al. Biological targeted therapies in patients with advanced enteropancreatic neuroendocrine carcinomas. Cancer Treat Rev 2010; 36:S87–S94. - PubMed
-
- Vinik A. Advances in diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Endocr Pract 2014; 20:1222–1230. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

