A comparative study of SVDquartets and other coalescent-based species tree estimation methods
- PMID: 26449249
- PMCID: PMC4602346
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-16-S10-S2
A comparative study of SVDquartets and other coalescent-based species tree estimation methods
Abstract
Background: Species tree estimation is challenging in the presence of incomplete lineage sorting (ILS), which can make gene trees different from the species tree. Because ILS is expected to occur and the standard concatenation approach can return incorrect trees with high support in the presence of ILS, "coalescent-based" summary methods (which first estimate gene trees and then combine gene trees into a species tree) have been developed that have theoretical guarantees of robustness to arbitrarily high amounts of ILS. Some studies have suggested that summary methods should only be used on "c-genes" (i.e., recombination-free loci) that can be extremely short (sometimes fewer than 100 sites). However, gene trees estimated on short alignments can have high estimation error, and summary methods tend to have high error on short c-genes. To address this problem, Chifman and Kubatko introduced SVDquartets, a new coalescent-based method. SVDquartets takes multi-locus unlinked single-site data, infers the quartet trees for all subsets of four species, and then combines the set of quartet trees into a species tree using a quartet amalgamation heuristic. Yet, the relative accuracy of SVDquartets to leading coalescent-based methods has not been assessed.
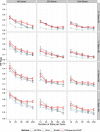
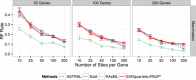
Results: We compared SVDquartets to two leading coalescent-based methods (ASTRAL-2 and NJst), and to concatenation using maximum likelihood. We used a collection of simulated datasets, varying ILS levels, numbers of taxa, and number of sites per locus. Although SVDquartets was sometimes more accurate than ASTRAL-2 and NJst, most often the best results were obtained using ASTRAL-2, even on the shortest gene sequence alignments we explored (with only 10 sites per locus). Finally, concatenation was the most accurate of all methods under low ILS conditions.
Conclusions: ASTRAL-2 generally had the best accuracy under higher ILS conditions, and concatenation had the best accuracy under the lowest ILS conditions. However, SVDquartets was competitive with the best methods under conditions with low ILS and small numbers of sites per locus. The good performance under many conditions of ASTRAL-2 in comparison to SVDquartets is surprising given the known vulnerability of ASTRAL-2 and similar methods to short gene sequences.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SVDquest: Improving SVDquartets species tree estimation using exact optimization within a constrained search space.Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2018 Jul;124:122-136. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2018.03.006. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2018. PMID: 29530498
-
To Include or Not to Include: The Impact of Gene Filtering on Species Tree Estimation Methods.Syst Biol. 2018 Mar 1;67(2):285-303. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syx077. Syst Biol. 2018. PMID: 29029338
-
ASTRID: Accurate Species TRees from Internode Distances.BMC Genomics. 2015;16 Suppl 10(Suppl 10):S3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-16-S10-S3. Epub 2015 Oct 2. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26449326 Free PMC article.
-
Implementing and testing the multispecies coalescent model: A valuable paradigm for phylogenomics.Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2016 Jan;94(Pt A):447-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2015.10.027. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2016. PMID: 26518740 Review.
-
Challenges in Species Tree Estimation Under the Multispecies Coalescent Model.Genetics. 2016 Dec;204(4):1353-1368. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.190173. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27927902 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring Conflicts in Whole Genome Phylogenetics: A Case Study Within Manakins (Aves: Pipridae).Syst Biol. 2023 May 19;72(1):161-178. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syac062. Syst Biol. 2023. PMID: 36130303 Free PMC article.
-
IDXL: Species Tree Inference Using Internode Distance and Excess Gene Leaf Count.J Mol Evol. 2017 Aug;85(1-2):57-78. doi: 10.1007/s00239-017-9807-7. Epub 2017 Aug 23. J Mol Evol. 2017. PMID: 28835989
-
Genome-scale data reveal the role of hybridization in lichen-forming fungi.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 30;10(1):1497. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58279-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32001749 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenomic analysis of the Chilean clade of Liolaemus lizards (Squamata: Liolaemidae) based on sequence capture data.PeerJ. 2017 Oct 26;5:e3941. doi: 10.7717/peerj.3941. eCollection 2017. PeerJ. 2017. PMID: 29085750 Free PMC article.
-
SPECIES TREE INFERENCE FROM GENOMIC SEQUENCES USING THE LOG-DET DISTANCE.SIAM J Appl Algebr Geom. 2019;3(1):107-127. doi: 10.1137/18m1194134. Epub 2019 Mar 14. SIAM J Appl Algebr Geom. 2019. PMID: 33163826 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

