Regulation of mitochondrial oxidative stress by β-arrestins in cultured human cardiac fibroblasts
- PMID: 26449263
- PMCID: PMC4728312
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.019968
Regulation of mitochondrial oxidative stress by β-arrestins in cultured human cardiac fibroblasts
Abstract
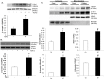
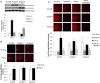
Oxidative stress in cardiac fibroblasts (CFs) promotes transformation to myofibroblasts and collagen synthesis leading to myocardial fibrosis, a precursor to heart failure (HF). NADPH oxidase 4 (Nox4) is a major source of cardiac reactive oxygen species (ROS); however, mechanisms of Nox4 regulation are unclear. β-arrestins are scaffold proteins that signal in G-protein-dependent and -independent pathways; for example, in ERK activation. We hypothesize that β-arrestins regulate oxidative stress in a Nox4-dependent manner and increase fibrosis in HF. CFs were isolated from normal and failing adult human left ventricles. Mitochondrial ROS/superoxide production was quantitated using MitoSox. β-arrestin and Nox4 expressions were manipulated using adenoviral overexpression or short interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated knockdown. Mitochondrial oxidative stress and Nox4 expression in CFs were significantly increased in HF. Nox4 knockdown resulted in inhibition of mitochondrial superoxide production and decreased basal and TGF-β-stimulated collagen and α-SMA expression. CF β-arrestin expression was upregulated fourfold in HF. β-arrestin knockdown in failing CFs decreased ROS and Nox4 expression by 50%. β-arrestin overexpression in normal CFs increased mitochondrial superoxide production twofold. These effects were prevented by inhibition of either Nox or ERK. Upregulation of Nox4 seemed to be a primary mechanism for increased ROS production in failing CFs, which stimulates collagen deposition. β-arrestin expression was upregulated in HF and plays an important and newly identified role in regulating mitochondrial superoxide production via Nox4. The mechanism for this effect seems to be ERK-mediated. Targeted inhibition of β-arrestins in CFs might decrease oxidative stress as well as pathological cardiac fibrosis.
Keywords: Cardiac fibroblast; Collagen; Heart failure; Myocardial fibrosis; NADPH oxidase; Oxidative stress; β-arrestin.
© 2015. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Regulation of cellular oxidative stress and apoptosis by G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2; The role of NADPH oxidase 4.Cell Signal. 2016 Mar;28(3):190-203. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.11.013. Epub 2015 Nov 27. Cell Signal. 2016. PMID: 26631573 Free PMC article.
-
β-Arrestins regulate human cardiac fibroblast transformation and collagen synthesis in adverse ventricular remodeling.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014 Nov;76:73-83. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Aug 15. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 25134464 Free PMC article.
-
Lysocardiolipin acyltransferase regulates TGF-β mediated lung fibroblast differentiation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Nov;112:162-173. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.07.023. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28751023
-
Stimulation of reactive oxygen species and collagen synthesis by angiotensin II in cardiac fibroblasts.Cardiovasc Ther. 2012 Feb;30(1):e1-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5922.2010.00205.x. Epub 2010 Jul 8. Cardiovasc Ther. 2012. PMID: 20626399 Review.
-
NADPH oxidase and cardiac failure.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2010 Aug;3(4):314-20. doi: 10.1007/s12265-010-9184-8. Epub 2010 Mar 31. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2010. PMID: 20559780 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Double life: How GRK2 and β-arrestin signaling participate in diseases.Cell Signal. 2022 Jun;94:110333. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2022.110333. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Cell Signal. 2022. PMID: 35430346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atorvastatin ameliorated myocardial fibrosis in db/db mice by inhibiting oxidative stress and modulating macrophage polarization.World J Diabetes. 2023 Dec 15;14(12):1849-1861. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i12.1849. World J Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 38222782 Free PMC article.
-
β-Arrestin Based Receptor Signaling Paradigms: Potential Therapeutic Targets for Complex Age-Related Disorders.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Nov 28;9:1369. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01369. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30546309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intersections between Copper, β-Arrestin-1, Calcium, FBXW7, CD17, Insulin Resistance and Atherogenicity Mediate Depression and Anxiety Due to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nomothetic Network Approach.J Pers Med. 2022 Jan 1;12(1):23. doi: 10.3390/jpm12010023. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35055338 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor mitigates osteoarthritis progression by inhibiting NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome activation and enhancing autophagy.PLoS One. 2021 Dec 23;16(12):e0256507. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256507. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34941874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al Ghouleh I., Khoo N. K. H., Knaus U. G., Griendling K. K., Touyz R. M., Thannickal V. J., Barchowsky A., Nauseef W. M., Kelley E. E., Bauer P. M. et al. (2011). Oxidases and peroxidases in cardiovascular and lung disease: new concepts in reactive oxygen species signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 51, 1271-1288. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.06.011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bristow M. R., Ginsburg R., Minobe W., Cubicciotti R. S., Sageman W. S., Lurie K., Billingham M. E., Harrison D. C. and Stinson E. B. (1982). Decreased catecholamine sensitivity and beta-adrenergic-receptor density in failing human hearts. N. Engl. J. Med. 307, 205-211. 10.1056/NEJM198207223070401 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

