Paradoxical effect of rapamycin on inflammatory stress-induced insulin resistance in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 26449763
- PMCID: PMC4598825
- DOI: 10.1038/srep14959
Paradoxical effect of rapamycin on inflammatory stress-induced insulin resistance in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
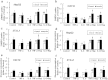
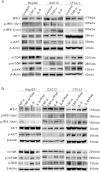
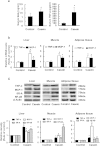
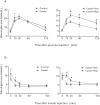
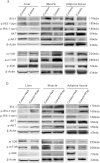
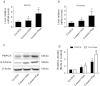
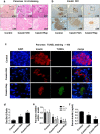
Insulin resistance is closely related to inflammatory stress and the mammalian target of rapamycin/S6 kinase (mTOR/S6K) pathway. The present study investigated whether rapamycin, a specific inhibitor of mTOR, ameliorates inflammatory stress-induced insulin resistance in vitro and in vivo. We used tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) stimulation in HepG2 hepatocytes, C2C12 myoblasts and 3T3-L1 adipocytes and casein injection in C57BL/6J mice to induce inflammatory stress. Our results showed that inflammatory stress impairs insulin signaling by reducing the expression of total IRS-1, p-IRS-1 (tyr632), and p-AKT (ser473); it also activates the mTOR/S6K signaling pathway both in vitro and in vivo. In vitro, rapamycin treatment reversed inflammatory cytokine-stimulated IRS-1 serine phosphorylation, increased insulin signaling to AKT and enhanced glucose utilization. In vivo, rapamycin treatment also ameliorated the impaired insulin signaling induced by inflammatory stress, but it induced pancreatic β-cell apoptosis, reduced pancreatic β-cell function and enhanced hepatic gluconeogenesis, thereby resulting in hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance in casein-injected mice. Our results indicate a paradoxical effect of rapamycin on insulin resistance between the in vitro and in vivo environments under inflammatory stress and provide additional insight into the clinical application of rapamycin.
Figures
References
-
- Biddinger S. B. & Kahn C. R. From mice to men: insights into the insulin resistance syndromes. Annu Rev Physiol 68, 123–158 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Lillioja S. et al. Insulin resistance and insulin secretory dysfunction as precursors of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Prospective studies of Pima Indians. N Engl J Med 329, 1988–1992 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Michael M. D. et al. Loss of insulin signaling in hepatocytes leads to severe insulin resistance and progressive hepatic dysfunction. Mol Cell 6, 87–97 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

