Agglutination Assays of the Plasmodium falciparum-Infected Erythrocyte
- PMID: 26450384
- PMCID: PMC6624126
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2815-6_10
Agglutination Assays of the Plasmodium falciparum-Infected Erythrocyte
Abstract
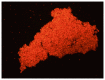
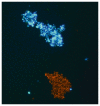
The agglutination assay is used to determine the ability of antibodies to recognize parasite variant antigens on the surface of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. In this technique, infected erythrocytes are selectively labelled with a DNA-binding fluorescent dye and mixed with antibodies of interest to allow antibody-surface antigen binding. Recognition of surface antigens by the antibodies can result in the formation of agglutinates containing multiple parasite-infected erythrocytes. These can be viewed and quantified using a fluorescence microscope.
Keywords: Agglutination; Antibody; Infected erythrocytes; Malaria; Naturally acquired immunity; PfEMP1; Plasmodium falciparum; Variant surface antigens.
Figures

References
-
- Aguiar JC, Albrecht GR, Cegielski P, et al. Agglutination of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes from East and West African isolates by human sera from distant geographic regions. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992;47:621–632. - PubMed
-
- Bull PC, Marsh K. The role of antibodies to Plasmodium falciparum-infected-erythrocyte surface antigens in naturally acquired immunity to malaria. Trends Microbiol. 2002;10:55–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

