Genetic sharing and heritability of paediatric age of onset autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 26450413
- PMCID: PMC4633631
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms9442
Genetic sharing and heritability of paediatric age of onset autoimmune diseases
Abstract
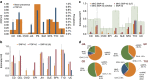
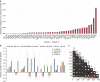
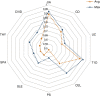
Autoimmune diseases (AIDs) are polygenic diseases affecting 7-10% of the population in the Western Hemisphere with few effective therapies. Here, we quantify the heritability of paediatric AIDs (pAIDs), including JIA, SLE, CEL, T1D, UC, CD, PS, SPA and CVID, attributable to common genomic variations (SNP-h(2)). SNP-h(2) estimates are most significant for T1D (0.863±s.e. 0.07) and JIA (0.727±s.e. 0.037), more modest for UC (0.386±s.e. 0.04) and CD (0.454±0.025), largely consistent with population estimates and are generally greater than that previously reported by adult GWAS. On pairwise analysis, we observed that the diseases UC-CD (0.69±s.e. 0.07) and JIA-CVID (0.343±s.e. 0.13) are the most strongly correlated. Variations across the MHC strongly contribute to SNP-h(2) in T1D and JIA, but does not significantly contribute to the pairwise rG. Together, our results partition contributions of shared versus disease-specific genomic variations to pAID heritability, identifying pAIDs with unexpected risk sharing, while recapitulating known associations between autoimmune diseases previously reported in adult cohorts.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- RC1 AR058606/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- C0482/MRF_/MRF_/United Kingdom
- RC1AR058606/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI061093/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR070549/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001425/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 AR066486/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1F30AR066486/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG006830/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- DP3 DK085708/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0800759/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- ETM/75/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- ETM/137/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- R18 AI048693/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR047363/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- DP3DK085708/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0800675/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600329/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HD052973/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006830/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

