Genotoxic stress inhibits Ewing sarcoma cell growth by modulating alternative pre-mRNA processing of the RNA helicase DHX9
- PMID: 26450900
- PMCID: PMC4741636
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5033
Genotoxic stress inhibits Ewing sarcoma cell growth by modulating alternative pre-mRNA processing of the RNA helicase DHX9
Abstract
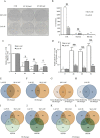
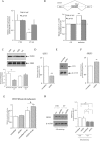
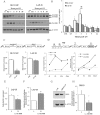
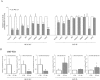
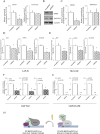
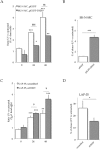
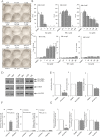
Alternative splicing plays a key role in the DNA damage response and in cancer. Ewing Sarcomas (ES) are aggressive tumors caused by different chromosomal translocations that yield in-frame fusion proteins driving transformation. RNA profiling reveals genes differentially regulated by UV light irradiation in two ES cell lines exhibiting different sensitivity to genotoxic stress. In particular, irradiation induces a new isoform of the RNA helicase DHX9 in the more sensitive SK-N-MC cells, which is targeted to nonsense-mediated decay (NMD), causing its downregulation. DHX9 protein forms a complex with RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) and EWS-FLI1 to enhance transcription. Silencing of DHX9 in ES cells sensitizes them to UV treatment and impairs recruitment of EWS-FLI1 to target genes, whereas DHX9 overexpression protects ES cells from genotoxic stress. Mechanistically, we found that UV light irradiation leads to enhanced phosphorylation and decreased processivity of RNAPII in SK-N-MC cells, which in turn causes inclusion of DHX9 exon 6A. A similar effect on DHX9 splicing was also elicited by treatment with the chemotherapeutic drug etoposide, indicating a more general mechanism of regulation in response to DNA damage. Our data identify a new NMD-linked splicing event in DHX9 with impact on EWS-FLI1 oncogenic activity and ES cell viability.
Keywords: DHX9; DNA damage; Ewing sarcoma; alternative splicing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Delattre O, Zucman J, Plougastel B, Desmaze C, Melot T, Peter M, Kovar H, Joubert I, de Jong P, Rouleau G, Aurias A, Thomas G. Gene fusion with an ETS DNA-binding domain caused by chromosome translocation in human tumours. Nature. 1992;359:162–5. - PubMed
-
- Riggi N, Stamenkovic I. The Biology of Ewing sarcoma. Cancer Lett. 2007;254:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

