T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase presents a novel therapeutic target in FLT3-ITD mutated acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 26450903
- PMCID: PMC4741775
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5418
T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase presents a novel therapeutic target in FLT3-ITD mutated acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
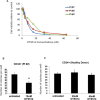
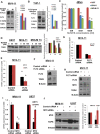
Gain-of-function mutations of FLT3 (FLT3-ITD), comprises up to 30% of normal karyotype acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and is associated with an adverse prognosis. Current FLT3 kinase inhibitors have been tested extensively, but have not yet resulted in a survival benefit and novel therapies are awaited. Here we show that T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase (TOPK), a mitotic kinase highly expressed in and correlated with more aggressive phenotype in several types of cancer, is expressed in AML but not in normal CD34+ cells and that TOPK knockdown decreased cell viability and induced apoptosis. Treatment of AML cells with TOPK inhibitor (OTS514) resulted in a dose-dependent decrease in cell viability with lower IC50 in FLT3-mutated cells, including blasts obtained from patients relapsed after FLT3-inhibitor treatment. Using a MV4-11-engrafted mouse model, we found that mice treated with 7.5 mg/kg IV daily for 3 weeks survived significantly longer than vehicle treated mice (median survival 46 vs 29 days, P < 0.001). Importantly, we identified TOPK as a FLT3-ITD and CEBPA regulated kinase, and that modulating TOPK expression or activity resulted in significant decrease of FLT3 expression and CEBPA phosphorylation. Thus, targeting TOPK in FLT3-ITD AML represents a novel therapeutic approach for this adverse risk subset of AML.
Keywords: AML; CEBPA; FLT3-ITD; TOPK; kinase inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
N.T, T.M, S.H, and Y.M are employees of OncoTherapy Science, Inc. Y.N is a stock holder and was a scientific advisor for OncoTherapy Science, Inc. J.-H.P is a scientific advisor for OncoTherapy Science, Inc. The authors have no additional financial interests.
Figures





References
-
- Whitman SP, Maharry K, Radmacher MD, Becker H, Mrozek K, Margeson D, Holland KB, Wu YZ, Schwind S, Metzeler KH, Wen J, Baer MR, Powell BL, et al. FLT3 internal tandem duplication associates with adverse outcome and gene- and microRNA-expression signatures in patients 60 years of age or older with primary cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia: a Cancer and Leukemia Group B study. Blood. 2010;116:3622–6. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beran M, Luthra R, Kantarjian H, Estey E. FLT3 mutation and response to intensive chemotherapy in young adult and elderly patients with normal karyotype. Leuk Res. 2004;28:547–50. - PubMed
-
- Krause DS, Van Etten RA. Tyrosine kinases as targets for cancer therapy. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:172–87. - PubMed
-
- Weisberg E, Sattler M, Ray A, Griffin JD. Drug resistance in mutant FLT3-positive AML. Oncogene. 2010;29:5120–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

