Investigation of enzyme-sensitive lipid nanoparticles for delivery of siRNA to blood-brain barrier and glioma cells
- PMID: 26451106
- PMCID: PMC4590347
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S87334
Investigation of enzyme-sensitive lipid nanoparticles for delivery of siRNA to blood-brain barrier and glioma cells
Abstract
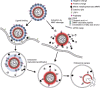
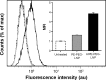
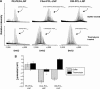
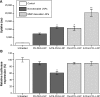
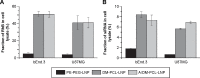
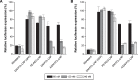
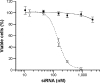
Clinical applications of siRNA for treating disorders in the central nervous system require development of systemic stable, safe, and effective delivery vehicles that are able to cross the impermeable blood-brain barrier (BBB). Engineering nanocarriers with low cellular interaction during systemic circulation, but with high uptake in targeted cells, is a great challenge and is further complicated by the BBB. As a first step in obtaining such a delivery system, this study aims at designing a lipid nanoparticle (LNP) able to efficiently encapsulate siRNA by a combination of titratable cationic lipids. The targeted delivery is obtained through the design of a two-stage system where the first step is conjugation of angiopep to the surface of the LNP for targeting the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 expressed on the BBB. Second, the positively charged LNPs are masked with a negatively charged PEGylated (poly(ethylene glycol)) cleavable lipopeptide, which contains a recognition sequence for matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), a class of enzymes often expressed in the tumor microenvironment and inflammatory BBB conditions. Proteolytic cleavage induces PEG release, including the release of four glutamic acid residues, providing a charge switch that triggers a shift of the LNP charge from weakly negative to positive, thus favoring cellular endocytosis and release of siRNA for high silencing efficiency. This work describes the development of this two-stage nanocarrier-system and evaluates the performance in brain endothelial and glioblastoma cells with respect to uptake and gene silencing efficiency. The ability of activation by MMP-triggered dePEGylation and charge shift is demonstrated to substantially increase the uptake and the silencing efficiency of the LNPs.
Keywords: BBB; angiopep; cleavable PEG-lipid; gene therapy; matrix metalloproteinase; nanocarrier.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peptide-like Polymers Exerting Effective Glioma-Targeted siRNA Delivery and Release for Therapeutic Application.Small. 2015 Oct;11(38):5142-50. doi: 10.1002/smll.201501167. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Small. 2015. PMID: 26222334
-
Amphetamine decorated cationic lipid nanoparticles cross the blood-brain barrier: therapeutic promise for combating glioblastoma.J Mater Chem B. 2020 May 21;8(19):4318-4330. doi: 10.1039/c9tb02700a. Epub 2020 Apr 24. J Mater Chem B. 2020. PMID: 32330214
-
Enhanced blood-brain barrier penetration and glioma therapy mediated by a new peptide modified gene delivery system.Biomaterials. 2015 Jan;37:345-52. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.10.034. Epub 2014 Oct 25. Biomaterials. 2015. PMID: 25453963
-
The role of helper lipids in lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) designed for oligonucleotide delivery.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016 Apr 1;99(Pt A):129-137. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2016.01.022. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016. PMID: 26900977 Review.
-
Lipid Nanoparticle Technology for Clinical Translation of siRNA Therapeutics.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Sep 17;52(9):2435-2444. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00368. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31397996 Review.
Cited by
-
Surface Functionalized Lipid Nanoparticles in Promoting Therapeutic Outcomes: An Insight View of the Dynamic Drug Delivery System.Curr Drug Targets. 2024;25(4):278-300. doi: 10.2174/0113894501285598240216065627. Curr Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38409709 Review.
-
Biological implications and clinical potential of invasion and migration related miRNAs in glioma.Front Integr Neurosci. 2022 Nov 21;16:989029. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2022.989029. eCollection 2022. Front Integr Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36479040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
pH-sensitive PEGylation of RIPL peptide-conjugated nanostructured lipid carriers: design and in vitro evaluation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Oct 23;13:6661-6675. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S184355. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30425481 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical applications of oligonucleotides for cancer therapy.Mol Ther. 2025 Jun 4;33(6):2705-2718. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2025.02.045. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Mol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40045578 Review.
-
Recent advances in siRNA delivery mediated by lipid-based nanoparticles.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;154-155:64-78. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.07.022. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020. PMID: 32768564 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbott NJ, Patabendige AA, Dolman DE, Yusof SR, Begley DJ. Structure and function of the blood–brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis. 2010;37(1):13–25. - PubMed
-
- Abbott NJ. Blood-brain barrier structure and function and the challenges for CNS drug delivery. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2013;36(3):437–449. - PubMed
-
- Huang R, Ma H, Guo Y, et al. Angiopep-conjugated nanoparticles for targeted long-term gene therapy of Parkinson’s disease. Pharm Res. 2013;30(10):2549–2559. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

