Elevated IgG4 in patient circulation is associated with the risk of disease progression in melanoma
- PMID: 26451312
- PMCID: PMC4590000
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2015.1032492
Elevated IgG4 in patient circulation is associated with the risk of disease progression in melanoma
Abstract
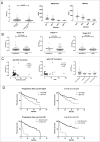
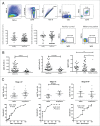
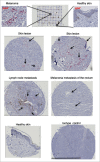
Emerging evidence suggests pathological and immunoregulatory functions for IgG4 antibodies and IgG4+ B cells in inflammatory diseases and malignancies. We previously reported that IgG4 antibodies restrict activation of immune effector cell functions and impair humoral responses in melanoma. Here, we investigate IgG4 as a predictor of risk for disease progression in a study of human sera (n = 271: 167 melanoma patients; 104 healthy volunteers) and peripheral blood B cells (n = 71: 47 melanoma patients; 24 healthy volunteers). IgG4 (IgG4/IgGtotal) serum levels were elevated in melanoma. High relative IgG4 levels negatively correlated with progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival. In early stage (I-II) disease, serum IgG4 was independently negatively prognostic for progression-free survival, as was elevation of IgG4+ circulating B cells (CD45+CD22+CD19+CD3-CD14-). In human tissues (n = 256; 108 cutaneous melanomas; 56 involved lymph nodes; 60 distant metastases; 32 normal skin samples) IgG4+ cell infiltrates were found in 42.6% of melanomas, 21.4% of involved lymph nodes and 30% of metastases, suggesting inflammatory conditions that favor IgG4 at the peripheral and local levels. Consistent with emerging evidence for an immunosuppressive role for IgG4, these findings indicate association of elevated IgG4 with disease progression and less favorable clinical outcomes. Characterizing immunoglobulin and other humoral immune profiles in melanoma might identify valuable prognostic tools for patient stratification and in the future lead to more effective treatments less prone to tumor-induced blockade mechanisms.
Keywords: B cells; IgG4; biomarker; cancer inflammation; humoral response; immunomodulation; immunomonitoring; immunosuppression; melanoma; prognosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IgG4 subclass antibodies impair antitumor immunity in melanoma.J Clin Invest. 2013 Apr;123(4):1457-74. doi: 10.1172/JCI65579. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23454746 Free PMC article.
-
IgG subclass switching and clonal expansion in cutaneous melanoma and normal skin.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 14;6:29736. doi: 10.1038/srep29736. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27411958 Free PMC article.
-
IgG4 induces tolerogenic M2-like macrophages and correlates with disease progression in colon cancer.Oncoimmunology. 2021 Feb 8;10(1):1880687. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2021.1880687. Oncoimmunology. 2021. PMID: 33628623 Free PMC article.
-
On the role of IgG4 in inflammatory conditions: lessons for IgG4-related disease.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 Apr;1864(4 Pt B):1401-1409. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.07.038. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 28782655 Review.
-
IgG4-related disease: why is it so important?Cent Eur J Immunol. 2018;43(2):204-208. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2018.77391. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30135634 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Colon cancer and IgG4-related disease with orbital inflammation and bilateral optic perineuritis: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Sep;97(39):e12197. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012197. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30278491 Free PMC article.
-
Serum IgG Is Associated With Risk of Melanoma in the Swedish AMORIS Study.Front Oncol. 2019 Oct 29;9:1095. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01095. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31737561 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive immune changes in colorectal cancer: a focus on T and B cell activation genes.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jun 8;16(1):1032. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02794-8. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40484866 Free PMC article.
-
A novel proangiogenic B cell subset is increased in cancer and chronic inflammation.Sci Adv. 2020 May 13;6(20):eaaz3559. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz3559. eCollection 2020 May. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32426497 Free PMC article.
-
B Cells in Patients With Melanoma: Implications for Treatment With Checkpoint Inhibitor Antibodies.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 25;11:622442. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.622442. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33569063 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J, Dummer R, Garbe C, Testori A, Maio M, et al.. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med 2011; 364:2507-16; PMID:21639808; http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1103782 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hodi FS, O'Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB, Gonzalez R, Robert C, Schadendorf D, Hassel JC, et al.. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl JMed 2010; 363:711-23; PMID:20525992; http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1003466 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corrie PG, Marshall A, Dunn JA, Middleton MR, Nathan PD, Gore M, Davidson N, Nicholson S, Kelly CG, Marples M, et al.. Adjuvant bevacizumab in patients with melanoma at high risk of recurrence (AVAST-M): preplanned interim results from a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 2014; 15:620-30; PMID:24745696; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70110-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Balch CM, Gershenwald JE, Soong SJ, Thompson JF, Atkins MB, Byrd DR, Buzaid AC, Cochran AJ, Coit DG, Ding S, et al.. Final version of 2009 AJCC melanoma staging and classification. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27:6199-206; PMID:19917835; http://dx.doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.23.4799 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Vries M, Speijers MJ, Bastiaannet E, Plukker JT, Brouwers AH, van Ginkel RJ, Suurmeijer AJ, Hoekstra HJ. Long-term follow-up reveals that ulceration and sentinel lymph node status are the strongest predictors for survival in patients with primary cutaneous melanoma. Eur J Surg Oncol 2011; 37:681-7; PMID:21636244; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2011.05.003 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
