Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model to Assess the Influence of Blinatumomab-Mediated Cytokine Elevations on Cytochrome P450 Enzyme Activity
- PMID: 26451330
- PMCID: PMC4592530
- DOI: 10.1002/psp4.12003
Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model to Assess the Influence of Blinatumomab-Mediated Cytokine Elevations on Cytochrome P450 Enzyme Activity
Abstract
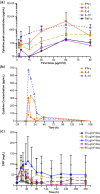
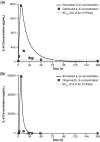
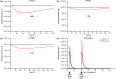
Blinatumomab is a CD19/CD3 bispecific T-cell engager (BiTE®) antibody construct for treatment of leukemia. Transient elevation of cytokines (interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10, interferon-gamma (IFN-γ)) has been observed within the first 48 hours of continuous intravenous blinatumomab infusion. In human hepatocytes, blinatumomab showed no effect on cytochrome P450 (CYP450) activities, whereas a cytokine cocktail showed suppression of CYP3A4, CYP1A2, and CYP2C9 activities. We developed a physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model to evaluate the effect of transient elevation of cytokines, particularly IL-6, on CYP450 suppression. The predicted suppression of hepatic CYP450 activities was <30%, and IL-6-mediated changes in exposure to sensitive substrates of CYP3A4, CYP1A2, and CYP2C9 were <twofold and lasted <1 week. Model verification indicated that IL-6 was the key cytokine suppressing CYP450 activities; the duration of cytokine elevation was a major determinant of magnitude of suppression. This study shows the utility of PBPK modeling for risk assessment of cytokine-mediated drug interactions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the potential impact on pharmacokinetics of various cytochrome P450 substrates of increasing IL-6 levels following administration of the T-cell bispecific engager glofitamab.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2024 Mar;13(3):396-409. doi: 10.1002/psp4.13091. Epub 2023 Dec 14. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38044486 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Drug-Drug Interaction Potential of Talquetamab, a T-Cell-Redirecting GPRC5D × CD3 Bispecific Antibody, as a Result of Cytokine Release Syndrome in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma in MonumenTAL-1, Using a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model.Target Oncol. 2024 Nov;19(6):965-979. doi: 10.1007/s11523-024-01093-6. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Target Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39285155 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Blinatumomab, a Bispecific T-cell Engager (BiTE(®)) for CD-19 Targeted Cancer Immunotherapy: Clinical Pharmacology and Its Implications.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2016 Oct;55(10):1271-1288. doi: 10.1007/s40262-016-0405-4. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2016. PMID: 27209293 Clinical Trial.
-
Blinatumomab: a CD19/CD3 bispecific T cell engager (BiTE) with unique anti-tumor efficacy.Leuk Lymphoma. 2016 May;57(5):1021-32. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2016.1161185. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Leuk Lymphoma. 2016. PMID: 27050240 Review.
-
Potential for bispecific T-cell engagers: role of blinatumomab in acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Feb 18;10:757-65. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S83848. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 26937176 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Population Pharmacokinetics of Upadacitinib in Healthy Subjects and Subjects with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Analyses of Phase I and II Clinical Trials.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018 Aug;57(8):977-988. doi: 10.1007/s40262-017-0605-6. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018. PMID: 29076110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the potential impact on pharmacokinetics of various cytochrome P450 substrates of increasing IL-6 levels following administration of the T-cell bispecific engager glofitamab.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2024 Mar;13(3):396-409. doi: 10.1002/psp4.13091. Epub 2023 Dec 14. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38044486 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating drug interaction potential from cytokine release syndrome using a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model: A case study of teclistamab.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2024 Jul;13(7):1117-1129. doi: 10.1002/psp4.13144. Epub 2024 Jun 3. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38831634 Free PMC article.
-
Current trends in drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2019 Nov;9(6):1113-1144. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2019.10.001. Epub 2019 Oct 18. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2019. PMID: 31867160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex Drug-Drug-Gene-Disease Interactions Involving Cytochromes P450: Systematic Review of Published Case Reports and Clinical Perspectives.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018 Oct;57(10):1267-1293. doi: 10.1007/s40262-018-0650-9. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018. PMID: 29667038
References
-
- Bargou R, et al. Tumor regression in cancer patients by very low doses of a T cell-engaging antibody. Science. 2008;321:974–977. - PubMed
-
- Nagorsen D. Baeuerle PA. Immunomodulatory therapy of cancer with T cell-engaging BiTE antibody blinatumomab. Exp. Cell Res. 2011;317:1255–1260. - PubMed
-
- Gore L, et al. 2013. . Cytological and molecular remissions with blinatumomab treatment in second or later bone marrow relapse in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting; May 31–June 4; Chicago, IL;
-
- Hijazi Y, et al. Blinatumomab exposure and pharmacodynamic response in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) J. Clin. Oncol. 2013;31 , abstract 3051 ( )
-
- Klinger M, et al. Immunopharmacologic response of patients with B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia to continuous infusion of T cell-engaging CD19/CD3-bispecific BiTE antibody blinatumomab. Blood. 2012;119:6226–6233. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

