Microbiota and the control of blood-tissue barriers
- PMID: 26451344
- PMCID: PMC4574894
- DOI: 10.1080/21688370.2015.1039691
Microbiota and the control of blood-tissue barriers
Abstract
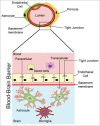
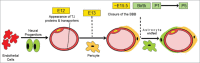
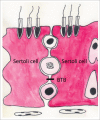
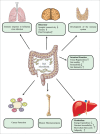
The gastro-intestinal tract is an ecosystem containing trillions of commensal bacteria living in symbiosis with the host. These microbiota modulate a variety of our physiological processes, including production of vitamins, absorption of nutrients and development of the immune system. One of their major functions is to fortify the intestinal barrier, thereby helping to prevent pathogens and harmful substances from crossing into the general circulation. Recently, effects of these microbiota on other blood-tissue barriers have also been reported. Here, we review the evidence indicating that gut bacteria play a role in regulating the blood-brain and blood-testis barriers. The underlying mechanisms include control of the expression of tight junction proteins by fermentation products such as butyrate, which also influences the activity of histone deacetylase.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier; blood-testis barrier; butyrate; intestinal barrier; microbiota; short chain fatty acids; tight junctions.
Figures

References
-
- Ribbert H. Die Abscheidung intravenos injizierten gelosten Karmins in den Geweben. Z Allgem Physiol 1904; 4:201-14
-
- Goldmann EE. [Die aüßere und innere Sekretion des gesunden und kranken Organismus im Lichte der “vitalen Farbung”]. Beitr Klin Chir 1909; 64:192-265
-
- Cheng CY, Mruk DD. The blood-testis barrier and its implications for male contraception. Pharmacol Rev 2012; 64:16-64; PMID:22039149; http://dx.doi.org/10.1124/pr.110.002790 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abbott NJ, Ronnback L, Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci 2006; 7:41-53; PMID:16371949; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrn1824 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ransom BR. The neuronal microenvironment In: Boron WF, Boulpaep E., ed. Medical Physiology (BORON). Philadelphia: Saunders, 2009:298-301
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
