Amphiregulin activates regulatory T lymphocytes and suppresses CD8+ T cell-mediated anti-tumor response in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- PMID: 26451607
- PMCID: PMC4741664
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5171
Amphiregulin activates regulatory T lymphocytes and suppresses CD8+ T cell-mediated anti-tumor response in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Abstract
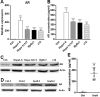
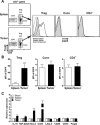
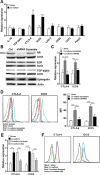
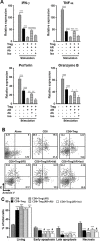
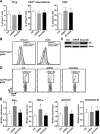
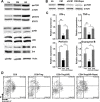
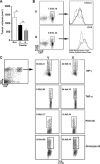
CD8+ T cell-mediated immune response plays an important role in inhibiting progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). For strategic immunotherapy, it is critical to understand why some of the tumor cells escape from this immune attack. In this study, we investigated how HCC cells alter endogenous anti-tumor immunity and their related signaling pathways. We found that HCC cells, both in vitro and in vivo, substantially secret and express amphiregulin (AR). AR in turn activates immunosuppressive function of intratumoral CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs), a major inhibitor of CD8+ T cells. Using either lentiviral siRNA, or AR neutralizing antibody, we blocked the expression and function of AR to test the specificity of AR mediated activation of Tregs, Biochemical and cell biology studies were followed and confirmed that blocking of AR inhibited Tregs activation. In addition, we found that AR can trigger the activation of rapamycin complex 1(mTORC1) signaling in Tregs. The mTORC1 inhibitor rapamycin treatment led to compromise Treg function and resulted in enhancing anti-tumor function of CD8+ T cells. Blocking AR/EGFR signaling in Tregs with Gefitinib also enhanced anti-tumor immunity and decreased tumor size in a mouse xenograft tumor model. Taken together, our study suggested a novel mechanism of functional interaction between HCC and Tregs for regulating anti-tumor function of CD8+ T cells.
Keywords: CD4+ regulatory T cells; CD8+ T cells; amphiregulin; hepatocellular carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sorafenib relieves cell-intrinsic and cell-extrinsic inhibitions of effector T cells in tumor microenvironment to augment antitumor immunity.Int J Cancer. 2014 Jan 15;134(2):319-31. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28362. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Int J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 23818246
-
Tumor-infiltrating FoxP3+ Tregs and CD8+ T cells affect the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients.Digestion. 2012;86(4):329-37. doi: 10.1159/000342801. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Digestion. 2012. PMID: 23207161
-
Regulatory T cell depletion enhances tumor specific CD8 T-cell responses, elicited by tumor antigen NY-ESO-1b in hepatocellular carcinoma patients, in vitro.Int J Oncol. 2010 Apr;36(4):841-8. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000561. Int J Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20198327
-
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and hepatocellular carcinoma: pathology and clinical management.Int J Clin Oncol. 2010 Dec;15(6):552-8. doi: 10.1007/s10147-010-0131-0. Epub 2010 Oct 21. Int J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20963618 Review.
-
Roles of Tregs in development of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jun 28;20(24):7971-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7971. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24976734 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kinome Profiling of Regulatory T Cells: A Closer Look into a Complex Intracellular Network.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 16;11(2):e0149193. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149193. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26881744 Free PMC article.
-
Amphiregulin promotes activated regulatory T cell-suppressive function via the AREG/EGFR pathway in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Head Face Med. 2024 Oct 26;20(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13005-024-00466-6. Head Face Med. 2024. PMID: 39456084 Free PMC article.
-
Multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells play critical roles in hepatocellular carcinoma initiation, progression and therapy.Mol Cancer. 2018 Dec 28;17(1):178. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0926-6. Mol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30593276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Complimenting the Complement": Mechanistic Insights and Opportunities for Therapeutics in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 24;10:627701. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.627701. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33718121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FOXP3 expression in FOXP3+ tumor cells promotes hepatocellular cells metastasis.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Oct;9(10):5868-5881. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-1875. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117200 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mizukoshi E, Nakamoto Y, Arai K, Yamashita T, Sakai A, Sakai Y, et al. Comparative analysis of various tumor-associated antigen-specific t-cell responses in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2011;53:1206–16. - PubMed
-
- Korangy F, Ormandy LA, Bleck JS, Klempnauer J, Wilkens L, Manns MP, et al. Spontaneous tumor-specific humoral and cellular immune responses to NY-ESO-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:4332–41. - PubMed
-
- Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, Alvarez X, Cheng P, Mottram P, et al. Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat Med. 2004;10:942–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

