Illustrative case using the RISK21 roadmap and matrix: prioritization for evaluation of chemicals found in drinking water
- PMID: 26451723
- PMCID: PMC4732461
- DOI: 10.3109/10408444.2015.1082973
Illustrative case using the RISK21 roadmap and matrix: prioritization for evaluation of chemicals found in drinking water
Abstract
The HESI-led RISK21 effort has developed a framework supporting the use of twenty-first century technology in obtaining and using information for chemical risk assessment. This framework represents a problem formulation-based, exposure-driven, tiered data acquisition approach that leads to an informed decision on human health safety to be made when sufficient evidence is available. It provides a transparent and consistent approach to evaluate information in order to maximize the ability of assessments to inform decisions and to optimize the use of resources. To demonstrate the application of the framework's roadmap and matrix, this case study evaluates a large number of chemicals that could be present in drinking water. The focus is to prioritize which of these should be considered for human health risk as individual contaminants. The example evaluates 20 potential drinking water contaminants, using the tiered RISK21 approach in combination with graphical representation of information at each step, using the RISK21 matrix. Utilizing the framework, 11 of the 20 chemicals were assigned low priority based on available exposure data alone, which demonstrated that exposure was extremely low. The remaining nine chemicals were further evaluated, using refined estimates of toxicity based on readily available data, with three deemed high priority for further evaluation. In the present case study, it was determined that the greatest value of additional information would be from improved exposure models and not from additional hazard characterization.
Keywords: Drinking water; RISK21; integrated evaluation strategy; prioritization; risk assessment; tiered approach.
Figures
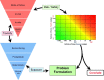

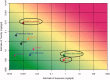
Comment in
-
Letter to the editor RE: Wolf et al. 1.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2016 Nov;46(10):911-912. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2016.1240657. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27750465 No abstract available.
-
Response to letter to the editor from Chappelle, Spence, and Tury concerning Wolf et al. 2016: Illustrative case using the RISK21 roadmap and matrix: prioritization for evaluation of chemicals found in drinking water. 2016, Crit. Rev. Toxicol. Vol 46: 43-53.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2016 Nov;46(10):913-914. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2016.1240658. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27805461 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Use of the RISK21 roadmap and matrix: human health risk assessment of the use of a pyrethroid in bed netting.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2016;46(1):54-73. doi: 10.3109/10408444.2015.1082974. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26517449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk assessment in the 21st century: roadmap and matrix.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2014 Aug;44 Suppl 3:6-16. doi: 10.3109/10408444.2014.931924. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 25070414 Review.
-
Using exposure bands for rapid decision making in the RISK21 tiered exposure assessment.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2017 Apr;47(4):317-341. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2016.1270255. Epub 2017 Feb 10. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28266262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A 21st century roadmap for human health risk assessment.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2014 Aug;44 Suppl 3:1-5. doi: 10.3109/10408444.2014.931923. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 25070413 Review.
-
A framework for cumulative risk assessment in the 21st century.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2017 Feb;47(2):85-97. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2016.1211618. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27685779 Review.
Cited by
-
Risk assessment of aflatoxin B1 in herbal medicines and plant food supplements marketed in Malaysia using margin of exposure and RISK21 approaches.Genes Environ. 2023 Nov 23;45(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s41021-023-00286-1. Genes Environ. 2023. PMID: 37993956 Free PMC article.
-
Utilizing Threshold of Toxicological Concern (TTC) with High Throughput Exposure Predictions (HTE) as a Risk-Based Prioritization Approach for thousands of chemicals.Comput Toxicol. 2018;7:58-67. doi: 10.1016/j.comtox.2018.07.002. Comput Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 31338483 Free PMC article.
-
Use of the RISK21 roadmap and matrix: human health risk assessment of the use of a pyrethroid in bed netting.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2016;46(1):54-73. doi: 10.3109/10408444.2015.1082974. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26517449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishing a quantitative framework for regulatory interpretation of genetic toxicity dose-response data: Margin of exposure case study of 48 compounds with both in vivo mutagenicity and carcinogenicity dose-response data.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2023 Jan;64(1):4-15. doi: 10.1002/em.22517. Epub 2023 Jan 6. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2023. PMID: 36345771 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of chemical-disease risk values to prioritize connections between environmental factors, genetic variants, and human diseases.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019 Sep 15;379:114674. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2019.114674. Epub 2019 Jul 16. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31323264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Council of Canadian Academies . Integrating emerging technologies into chemical safety assessment. Ottawa, Canada: Council of Canadian Academies; 2012.
-
- Cramer GM, Ford RA, Hall RL. Estimation of toxic hazard – a decision tree approach. Food Cosmetic Toxicol. 1978;16:255–276. - PubMed
-
- EFSA Draft scientific opinion on exploring options for providing preliminary advice about possible human health risks based on the concept of threshold of toxicological concern (TTC). EFSA J. 2012a;10:2750.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
