Reconstruction of ancestral gene orders using intermediate genomes
- PMID: 26451811
- PMCID: PMC4602182
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-16-S14-S3
Reconstruction of ancestral gene orders using intermediate genomes
Abstract
Background: The problem of reconstructing ancestral genomes in a given phylogenetic tree arises in many different comparative genomics fields. Here, we focus on reconstructing the gene order of ancestral genomes, a problem that has been largely studied in the past 20 years, especially with the increasing availability of whole genome DNA sequences. There are two main approaches to this problem: event-based methods, that try to find the ancestral genomes that minimize the number of rearrangement events in the tree; and homology-based, that look for conserved structures, such as adjacent genes in the extant genomes, to build the ancestral genomes.
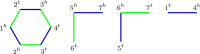
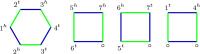
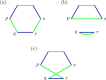
Results: We propose algorithms that use the concept of intermediate genomes, arising in optimal pairwise rearrangement scenarios. We show that intermediate genomes have combinatorial properties that make them easy to reconstruct, and develop fast algorithms with better reconstructed ancestral genomes than current event-based methods. The proposed framework is also designed to accept extra information, such as results from homology-based approaches, giving rise to combined algorithms with better results than the original methods.
Figures
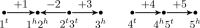





Similar articles
-
Fast ancestral gene order reconstruction of genomes with unequal gene content.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Nov 11;17(Suppl 14):413. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1261-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 28185578 Free PMC article.
-
Ancestral Genome Reconstruction on Whole Genome Level.Curr Genomics. 2017 Aug;18(4):306-315. doi: 10.2174/1389202918666170307120943. Curr Genomics. 2017. PMID: 29081686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SCJ Small Parsimony Problem for Weighted Gene Adjacencies.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2019 Jul-Aug;16(4):1364-1373. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2017.2661761. Epub 2017 Jan 31. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 28166504
-
ProCARs: Progressive Reconstruction of Ancestral Gene Orders.BMC Genomics. 2015;16 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):S6. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-16-S5-S6. Epub 2015 May 26. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26040958 Free PMC article.
-
Ancestral animal genomes reconstruction.Curr Opin Immunol. 2007 Oct;19(5):542-6. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2007.06.009. Epub 2007 Aug 15. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17702562 Review.
Cited by
-
Orthologs, turn-over, and remolding of tRNAs in primates and fruit flies.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 11;17(1):617. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2927-4. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27515907 Free PMC article.
-
SMORE: Synteny Modulator of Repetitive Elements.Life (Basel). 2017 Oct 31;7(4):42. doi: 10.3390/life7040042. Life (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29088079 Free PMC article.
-
Fast ancestral gene order reconstruction of genomes with unequal gene content.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Nov 11;17(Suppl 14):413. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1261-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 28185578 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics meets topology: a novel view on genome median and halving problems.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Nov 11;17(Suppl 14):418. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1263-7. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 28185564 Free PMC article.
-
Ancestral Genome Reconstruction on Whole Genome Level.Curr Genomics. 2017 Aug;18(4):306-315. doi: 10.2174/1389202918666170307120943. Curr Genomics. 2017. PMID: 29081686 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bergeron A, Mixtacki J, Stoye J. A unifying view of genome rearrangements. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 2006;4175:163–173. doi: 10.1007/11851561_16. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

