Caregiver-mediated exercises with e-health support for early supported discharge after stroke (CARE4STROKE): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 26452543
- PMCID: PMC4600217
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-015-0440-z
Caregiver-mediated exercises with e-health support for early supported discharge after stroke (CARE4STROKE): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Several systematic reviews have shown that additional exercise therapy has a positive effect on functional outcome after stroke. However, there is an urgent need for resource-efficient methods to augment rehabilitation services without increasing health care costs. Asking informal caregivers to do exercises with their loved ones, combined with e-health services may be a cost-effective method to promote early supported discharge with increased functional outcome. The primary aim of the CARE4STROKE study is to evaluate the effects and cost-effectiveness of a caregiver-mediated exercises program combined with e-health services after stroke in terms of self-reported mobility and length of stay.
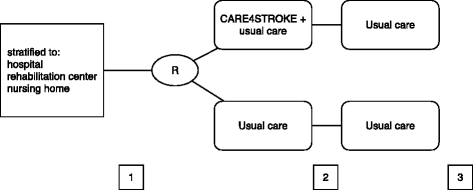
Methods: An observer-blinded randomized controlled trial, in which 66 stroke-patients admitted to a hospital stroke unit, rehabilitation center or nursing home are randomly assigned to either 8 weeks of the CARE4STROKE program in addition to usual care (i.e., experimental group) or 8 weeks of usual care alone (i.e., control group). The CARE4STROKE program is compiled in consultation with a trained physical therapist. A tablet computer is used to present video-based exercises for gait and gait-related activities in which a caregiver acts as an exercise coach. Primary outcomes are the mobility domain of the Stroke Impact Scale and length of stay. Secondary outcomes are the other domains of the Stroke Impact Scale, motor impairment, strength, walking ability, balance, mobility, (Extended) Activities of Daily Living, psychosocial functioning, self-efficacy, fatigue, health-related quality of life of the patient as well as the experienced strain, psychosocial functioning and quality of life of the caregiver. An economic evaluation will be conducted from the societal and health care perspective.
Discussion: The main aspects of the CARE4STROKE program are 1) increasing intensity of training by doing exercises with a caregiver in addition to usual care and 2) e-health support. We hypothesize this program leads to better functional outcome and early supported discharge, resulting in reduced costs.
Trial registration: The study is registered in the Dutch trial register as NTR4300, registered 2 December 2013.
Figures
References
-
- Feigin VL, Forouzanfar MH, Krishnamurthi R, Mensah GA, Connor M, Bennett DA, Moran AE, Sacco RL, Anderson L, Truelsen T, et al. Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990–2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2014;383(9913):245–254. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61953-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical