Interaction of the EGF Receptor and the Hippo Pathway in the Diabetic Kidney
- PMID: 26453611
- PMCID: PMC4884112
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2015040415
Interaction of the EGF Receptor and the Hippo Pathway in the Diabetic Kidney
Abstract
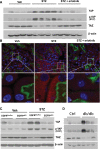
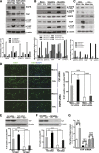
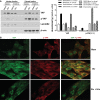
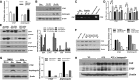
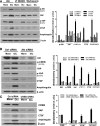
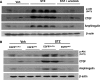
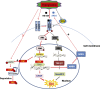
Activation of the EGF receptor (EGFR) or the Hippo signaling pathway can control cell proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation, and the dysregulation of these pathways can contribute to tumorigenesis. Previous studies showed that activation of EGFR signaling in renal epithelial cells can exacerbate diabetic kidney injury. Moreover, EGFR has been implicated in regulating the Hippo signaling pathway in Drosophila; thus, we examined this potential interaction in mammalian diabetic kidney disease. Yes-associated protein (YAP) is a transcriptional regulator regulated by the Hippo signaling pathway. We found YAP protein expression and phosphorylation were upregulated in diabetic mouse renal proximal tubule epithelial cells, which were inhibited in diabetic proximal tubule EGFR-knockout mice (EGFR(ptKO)) or administration of an EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib. Furthermore, activation of an EGFR-PI3K-Akt-CREB signaling pathway mediated YAP gene expression and YAP nuclear translocation and interaction with the TEA domain (TEAD) transcription factor complex, which led to upregulated expression of two TEAD-dependent genes, the connective tissue growth factor and amphiregulin genes. In a renal proximal tubule cell line, either pharmacologic or genetic inhibition of EGFR, Akt, or CREB blunted YAP expression in response to high-glucose treatment. Additionally, knocking down YAP expression by specific siRNA inhibited cell proliferation in response to high glucose or exogenous EGF. Therefore, these results link the Hippo pathway to EGFR-mediated renal epithelial injury in diabetes.
Keywords: cell signaling; diabetic nephropathy; epidermal growth factor.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
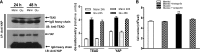
Similar articles
-
Targeting mammalian serine/threonine-protein kinase 4 through Yes-associated protein/TEA domain transcription factor-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition ameliorates diabetic nephropathy orchestrated renal fibrosis.Metabolism. 2020 Jul;108:154258. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154258. Epub 2020 May 3. Metabolism. 2020. PMID: 32376130
-
YAP mediates the interaction between the Hippo and PI3K/Akt pathways in mesangial cell proliferation in diabetic nephropathy.Acta Diabetol. 2021 Jan;58(1):47-62. doi: 10.1007/s00592-020-01582-w. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Acta Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 32816106
-
EGF Receptor-Dependent YAP Activation Is Important for Renal Recovery from AKI.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018 Sep;29(9):2372-2385. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2017121272. Epub 2018 Aug 2. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30072422 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of the mammalian Hippo signaling pathway.Yi Chuan. 2017 Jul 20;39(7):546-567. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.17-094. Yi Chuan. 2017. PMID: 28757470 Review.
-
Neuregulin 1-activated ERBB4 as a "dedicated" receptor for the Hippo-YAP pathway.Sci Signal. 2014 Dec 9;7(355):pe29. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaa2710. Sci Signal. 2014. PMID: 25492964 Review.
Cited by
-
EGFR inhibition attenuates diabetic nephropathy through decreasing ROS and endoplasmic reticulum stress.Oncotarget. 2017 May 16;8(20):32655-32667. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15948. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28427241 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin and Canagliflozin Are Equally Renoprotective in Diabetic Kidney Disease but Have No Synergistic Effect.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 20;24(10):9043. doi: 10.3390/ijms24109043. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240387 Free PMC article.
-
Podocyte EGFR Inhibits Autophagy Through Upregulation of Rubicon in Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy.Diabetes. 2021 Feb;70(2):562-576. doi: 10.2337/db20-0660. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 33239448 Free PMC article.
-
Proximal Tubule-Derived Amphiregulin Amplifies and Integrates Profibrotic EGF Receptor Signals in Kidney Fibrosis.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019 Dec;30(12):2370-2383. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019030321. Epub 2019 Nov 1. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31676723 Free PMC article.
-
Yap/Taz mediates mTORC2-stimulated fibroblast activation and kidney fibrosis.J Biol Chem. 2018 Oct 19;293(42):16364-16375. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004073. Epub 2018 Aug 28. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30154246 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caramori ML, Mauer M: Diabetes and nephropathy. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 12: 273–282, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Susztak K, Böttinger EP: Diabetic nephropathy: A frontier for personalized medicine. J Am Soc Nephrol 17: 361–367, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Schena FP, Gesualdo L: Pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 16[Suppl 1]: S30–S33, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Harris RC: Response of rat inner medullary collecting duct to epidermal growth factor. Am J Physiol 256: F1117–F1124, 1989 - PubMed
-
- Breyer MD, Redha R, Breyer JA: Segmental distribution of epidermal growth factor binding sites in rabbit nephron. Am J Physiol 259: F553–F558, 1990 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

