Assessment of the functionality and stability of detergent purified nAChR from Torpedo using lipidic matrixes and macroscopic electrophysiology
- PMID: 26454038
- PMCID: PMC4663142
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.10.002
Assessment of the functionality and stability of detergent purified nAChR from Torpedo using lipidic matrixes and macroscopic electrophysiology
Abstract
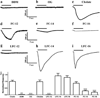
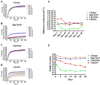
In our previous study we examined the functionality and stability of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR)-detergent complexes (nAChR-DCs) from affinity-purified Torpedo californica (Tc) using fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) in Lipidic Cubic Phase (LCP) and planar lipid bilayer (PLB) recordings for phospholipid and cholesterol like detergents. In the present study we enhanced the functional characterization of nAChR-DCs by recording macroscopic ion channel currents in Xenopus oocytes using the two electrode voltage clamp (TEVC). The use of TEVC allows for the recording of macroscopic currents elicited by agonist activation of nAChR-DCs that assemble in the oocyte plasma membrane. Furthermore, we examined the stability of nAChR-DCs, which is obligatory for the nAChR crystallization, using a 30 day FRAP assay in LCP for each detergent. The present results indicate a marked difference in the fractional fluorescence recovery (ΔFFR) within the same detergent family during the 30 day period assayed. Within the cholesterol analog family, sodium cholate and CHAPSO displayed a minimum ΔFFR and a mobile fraction (MF) over 80%. In contrast, CHAPS and BigCHAP showed a marked decay in both the mobile fraction and diffusion coefficient. nAChR-DCs containing phospholipid analog detergents with an alkylphosphocholine (FC) and lysofoscholine (LFC) of 16 carbon chains (FC-16, LFC-16) were more effective in maintaining a mobile fraction of over 80% compared to their counterparts with shorter acyl chain (C12, C14). The significant differences in macroscopic current amplitudes, activation and desensitization rates among the different nAChR-DCs evaluated in the present study allow to dissect which detergent preserves both, agonist activation and ion channel function. Functionality assays using TEVC demonstrated that LFC16, LFC14, and cholate were the most effective detergents in preserving macroscopic ion channel function, however, the nAChR-cholate complex display a significant delay in the ACh-induce channel activation. In summary, these results suggest that the physical properties of the lipid analog detergents (headgroup and acyl chain length) are the most effective in maintaining both the stability and functionality of the nAChR in the detergent solubilized complex.
Keywords: Detergents; Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching; Lipidic Cubic Phase; NAChR; Planar lipid bilayer; Two-electrode voltage clamp.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
We wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome. We confirm that the manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors and that there are no other persons who satisfied the criteria for authorship but are not listed. We further confirm that the order of authors listed in the manuscript has been approved by all of us. We confirm that we have given due consideration to the protection of intellectual property associated with this work and that there are no impediments to publication, including the timing of publication, with respect to intellectual property. In so doing we confirm that we have followed the regulations of our institutions concerning intellectual property. We further confirm that any aspect of the work covered in this manuscript that has involved either experimental animals or human patients has been conducted with the ethical approval of all relevant bodies and that such approvals are acknowledged within the manuscript. We understand that the Corresponding Author is the sole contact for the Editorial process. He is responsible for communicating with the other authors about progress, submissions of revisions and final approval of proofs. We confirm that we have provided a current, correct email address which is accessible by the Corresponding Author.
Figures
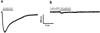
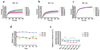
Similar articles
-
Assessment of Purity, Functionality, Stability, and Lipid Composition of Cyclofos-nAChR-Detergent Complexes from Torpedo californica Using Lipid Matrix and Macroscopic Electrophysiology.J Membr Biol. 2023 Jun;256(3):271-285. doi: 10.1007/s00232-023-00285-x. Epub 2023 May 4. J Membr Biol. 2023. PMID: 37140614 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the lipidic basis for the preparation of functional nicotinic acetylcholine receptor detergent complexes for structural studies.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 19;6:32766. doi: 10.1038/srep32766. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27641515 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of lipid-analog detergent solubilization on the functionality and lipidic cubic phase mobility of the Torpedo californica nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.J Membr Biol. 2011 Oct;243(1-3):47-58. doi: 10.1007/s00232-011-9392-4. Epub 2011 Sep 16. J Membr Biol. 2011. PMID: 21922299 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence Studies of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor and Its Associated Lipid Milieu: The Influence of Erwin London's Methodological Approaches.J Membr Biol. 2022 Oct;255(4-5):563-574. doi: 10.1007/s00232-022-00239-9. Epub 2022 May 9. J Membr Biol. 2022. PMID: 35534578 Review.
-
Crystallizing membrane proteins using lipidic bicelles.Methods. 2011 Dec;55(4):337-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2011.09.020. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Methods. 2011. PMID: 21982781 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pursuing High-Resolution Structures of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors: Lessons Learned from Five Decades.Molecules. 2021 Sep 23;26(19):5753. doi: 10.3390/molecules26195753. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34641297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of Purity, Functionality, Stability, and Lipid Composition of Cyclofos-nAChR-Detergent Complexes from Torpedo californica Using Lipid Matrix and Macroscopic Electrophysiology.J Membr Biol. 2023 Jun;256(3):271-285. doi: 10.1007/s00232-023-00285-x. Epub 2023 May 4. J Membr Biol. 2023. PMID: 37140614 Free PMC article.
-
Functionality and stability data of detergent purified nAChR from Torpedo using lipidic matrixes and macroscopic electrophysiology.Data Brief. 2015 Dec 25;6:433-7. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2015.12.010. eCollection 2016 Mar. Data Brief. 2015. PMID: 26870753 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the lipidic basis for the preparation of functional nicotinic acetylcholine receptor detergent complexes for structural studies.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 19;6:32766. doi: 10.1038/srep32766. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27641515 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential purification and characterization of Torpedo californica nAChR-DC supplemented with CHS for high-resolution crystallization studies.Anal Biochem. 2020 Dec 1;610:113887. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2020.113887. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Anal Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32763308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beeson D. Synaptic dysfunction in congenital myasthenic syndromes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012;1275:63–69. - PubMed
-
- Engel AG, Sine SM. Current understanding of congenital myasthenic syndromes. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2005;5:308–321. - PubMed
-
- Müller JS, Mihaylova V, Abicht A, Lochmüller H. Congenital myasthenic syndromes: spotlight on genetic defects of neuromuscular transmission. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2007;9:1–20. - PubMed
-
- Rodríguez Cruz PM, Sewry C, Beeson D, Jayawant S, Squier W, McWilliam R, Palace J. Congenital myopathies with secondary neuromuscular transmission defects; a case report and review of the literature. Neuromuscul. Disord. NMD. 2014;24:1103–1110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

