Serotonergic systems in the balance: CRHR1 and CRHR2 differentially control stress-induced serotonin synthesis
- PMID: 26454419
- PMCID: PMC4695240
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2015.09.024
Serotonergic systems in the balance: CRHR1 and CRHR2 differentially control stress-induced serotonin synthesis
Abstract
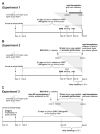
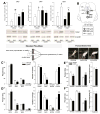
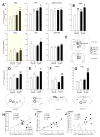
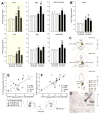
Anxiety and affective disorders are often associated with hypercortisolism and dysfunctional serotonergic systems, including increased expression of TPH2, the gene encoding the rate-limiting enzyme of neuronal serotonin synthesis. We previously reported that chronic glucocorticoid exposure is anxiogenic and increases rat Tph2 mRNA expression, but it was still unclear if this also translates to increased TPH2 protein levels and in vivo activity of the enzyme. Here, we found that adult male rats treated with corticosterone (CORT, 100 μg/ml) via the drinking water for 21 days indeed show increased TPH2 protein expression in the dorsal and ventral part of the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRD, DRV) during the light phase, abolishing the enzyme's diurnal rhythm. In a second study, we systemically blocked the conversion of 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) to serotonin immediately before rats treated with CORT or vehicle were either exposed to 30 min acoustic startle stress or home cage control conditions. This allowed us to measure 5-HTP accumulation as a direct readout of basal versus stress-induced in vivo TPH2 activity. As expected, basal TPH2 activity was elevated in the DRD, DRV and MnR of CORT-treated rats. In response to stress, a multitude of serotonergic systems reacted with increased TPH2 activity, but the stress-, anxiety-, and learned helplessness-related dorsal and caudal DR (DRD/DRC) displayed stress-induced increases in TPH2 activity only after chronic CORT-treatment. To address the mechanisms underlying this region-specific CORT-dependent sensitization, we stereotaxically implanted CORT-treated rats with cannulae targeting the DR, and pharmacologically blocked either corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor type 1 (CRHR1) or type 2 (CRHR2) 10 min prior to acoustic startle stress. CRHR2 blockade prevented stress-induced increases of TPH2 activity within the DRD/DRC, while blockade of CRHR1 potentiated stress-induced TPH2 activity in the entire DR. Stress-induced TPH2 activity in the DRD/DRC furthermore predicted TPH2 activity in the amygdala and in the caudal pontine reticular nucleus (PnC), while serotonin synthesis in the PnC was strongly correlated with the maximum startle response. Our data demonstrate that chronically elevated glucocorticoids sensitize stress- and anxiety-related serotonergic systems, and for the first time reveal competing roles of CRHR1 and CRHR2 on stress-induced in vivo serotonin synthesis.
Keywords: Corticotropin receptor; Dorsal raphe nucleus; Glucocorticoids; Serotonin; Stress; Tryptophan hydroxylase.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
The authors have no commercial interest and report no conflict of interest with regard to the submitted manuscript and the experiments conducted.
Figures

References
-
- Abrams JK, Johnson PL, Hay-Schmidt A, Mikkelsen JD, Shekhar A, Lowry CA. Serotonergic systems associated with arousal and vigilance behaviors following administration of anxiogenic drugs. Neuroscience. 2005;133:983–997. - PubMed
-
- Amat J, Tamblyn JP, Paul ED, Bland ST, Amat P, Foster AC, Watkins LR, Maier SF. Microinjection of urocortin 2 into the dorsal raphe nucleus activates serotonergic neurons and increases extracellular serotonin in the basolateral amygdala. Neuroscience. 2004;129:509–519. - PubMed
-
- Amilhon B, Lepicard E, Renoir T, Mongeau R, Popa D, Poirel O, Miot S, Gras C, Gardier AM, Gallego J, Hamon M, Lanfumey L, Gasnier B, Giros B, El Mestikawy S. VGLUT3 (vesicular glutamate transporter type 3) contribution to the regulation of serotonergic transmission and anxiety. J Neurosci. 2010;30:2198–2210. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Asan E, Steinke M, Lesch KP. Serotonergic innervation of the amygdala: targets, receptors, and implications for stress and anxiety. Histochem Cell Biol. 2013;139:785–813. - PubMed
-
- Bach-Mizrachi H, Underwood MD, Kassir SA, Bakalian MJ, Sibille E, Tamir H, Mann JJ, Arango V. Neuronal tryptophan hydroxylase mRNA expression in the human dorsal and median raphe nuclei: major depression and suicide. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006;31:814–824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

