Mice lacking GPR3 receptors display late-onset obese phenotype due to impaired thermogenic function in brown adipose tissue
- PMID: 26455425
- PMCID: PMC4601089
- DOI: 10.1038/srep14953
Mice lacking GPR3 receptors display late-onset obese phenotype due to impaired thermogenic function in brown adipose tissue
Abstract
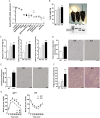
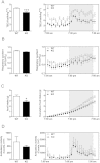
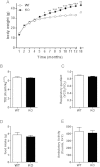
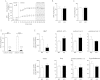
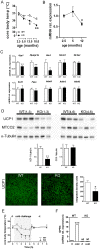
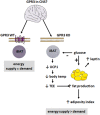
We report an unexpected link between aging, thermogenesis and weight gain via the orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR3. Mice lacking GPR3 and maintained on normal chow had similar body weights during their first 5 months of life, but gained considerably more weight thereafter and displayed reduced total energy expenditure and lower core body temperature. By the age of 5 months GPR3 KO mice already had lower thermogenic gene expression and uncoupling protein 1 protein level and showed impaired glucose uptake into interscapular brown adipose tissue (iBAT) relative to WT littermates. These molecular deviations in iBAT of GPR3 KO mice preceded measurable differences in body weight and core body temperature at ambient conditions, but were coupled to a failure to maintain thermal homeostasis during acute cold challenge. At the same time, the same cold challenge caused a 17-fold increase in Gpr3 expression in iBAT of WT mice. Thus, GPR3 appears to have a key role in the thermogenic response of iBAT and may represent a new therapeutic target in age-related obesity.
Figures
References
-
- Arterburn D. E., Crane P. K. & Sullivan S. D. The coming epidemic of obesity in elderly Americans. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 52, 1907–1912 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Flier J. S. Obesity wars: molecular progress confronts an expanding epidemic. Cell 116, 337–350 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Wang Y. C., McPherson K., Marsh T., Gortmaker S. L. & Brown M. Health and economic burden of the projected obesity trends in the USA and the UK. Lancet 378, 815–825 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

