Templated polymers enable selective capture and release of lysophosphatidic acid in human plasma via optimization of non-covalent binding to functional monomers
- PMID: 26455441
- PMCID: PMC4642816
- DOI: 10.1039/c5an01597a
Templated polymers enable selective capture and release of lysophosphatidic acid in human plasma via optimization of non-covalent binding to functional monomers
Abstract
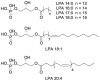
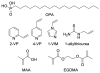
The first solid phase extraction materials for selective lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) enrichment from human plasma are described. Molecularly imprinted polymers were designed, synthesized and evaluated as cartridge fillings. They enabled a relatively rapid and simple extraction protocol for LPA without any need for multiple liquid-liquid extraction steps. The five major subspecies of lysophosphatidic acid are readily separated from all other native plasma phospholipids, including those well-known to interfere with LPA quantitation, such as phosphatidylcholine and lysophosphatidylcholine. Outstanding LPA purity is obtained via these solid phase materials in a tandem extraction setup.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Molecularly imprinted polymer for solid-phase extraction of ephedrine and analogs from human plasma.J Sep Sci. 2009 Apr;32(7):1036-42. doi: 10.1002/jssc.200800684. J Sep Sci. 2009. PMID: 19266546
-
Computer aided-molecular design and synthesis of a high selective molecularly imprinted polymer for solid-phase extraction of furosemide from human plasma.Anal Chim Acta. 2010 Jan 25;658(2):225-32. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2009.11.019. Epub 2009 Nov 16. Anal Chim Acta. 2010. PMID: 20103099
-
Molecularly imprinted polymer for specific extraction of hypericin from Hypericum perforatum L. herbal extract.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Sep;98:210-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2014.05.031. Epub 2014 May 29. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 24946147
-
Molecularly imprinted polymers and their application in solid phase extraction.J Sep Sci. 2009 Mar;32(5-6):799-812. doi: 10.1002/jssc.200800506. J Sep Sci. 2009. PMID: 19219838 Review.
-
[Application of molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction on drug residues in animal source foods].Se Pu. 2011 Jul;29(7):572-9. Se Pu. 2011. PMID: 22097780 Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Stähle M, Veit C, Bachfischer U, Schierling K, Skripczynski B, Hall A, Gierschik P, Giehl K. J. Cell Sci. 2003;116:3835–3846. - PubMed
-
- Jesionowska A, Cecerska E, Dolegowska B. Anal. Biochem. 2014;453:38–43. - PubMed
-
- Bligh EG, Dyer WJ. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959;37:911–917. - PubMed
-
- Baker DL, Desiderio DM, Miller DD, Tolley B, Tigyi GJ. Anal. Biochem. 2001;292:287–295. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y-L, Xu Y. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 2001;753:355–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

