Theta oscillations regulate the speed of locomotion via a hippocampus to lateral septum pathway
- PMID: 26455912
- PMCID: PMC4633825
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms9521
Theta oscillations regulate the speed of locomotion via a hippocampus to lateral septum pathway
Abstract
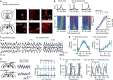
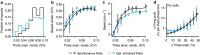
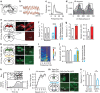
Hippocampal theta oscillations support encoding of an animal's position during spatial navigation, yet longstanding questions about their impact on locomotion remain unanswered. Combining optogenetic control of hippocampal theta oscillations with electrophysiological recordings in mice, we show that hippocampal theta oscillations regulate locomotion. In particular, we demonstrate that their regularity underlies more stable and slower running speeds during exploration. More regular theta oscillations are accompanied by more regular theta-rhythmic spiking output of pyramidal cells. Theta oscillations are coordinated between the hippocampus and its main subcortical output, the lateral septum (LS). Chemo- or optogenetic inhibition of this pathway reveals its necessity for the hippocampal regulation of running speed. Moreover, theta-rhythmic stimulation of LS projections to the lateral hypothalamus replicates the reduction of running speed induced by more regular hippocampal theta oscillations. These results suggest that changes in hippocampal theta synchronization are translated into rapid adjustment of running speed via the LS.
Figures

References
-
- Maurer A. P. & McNaughton B. L. Network and intrinsic cellular mechanisms underlying theta phase precession of hippocampal neurons. Trends Neurosci. 30, 325–333 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Vanderwolf C. H. Hippocampal electrical activity and voluntary movement in the rat. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 26, 407–418 (1969). - PubMed
-
- Grastyan E., Karmos G., Vereczkey L., Martin J. & Kellenyi L. Hypothalamic motivational processes as reflected by their hippocampal electrical correlates. Science 149, 91–93 (1965). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

