Fibronectin-binding protein TDE1579 affects cytotoxicity of Treponema denticola
- PMID: 26456217
- PMCID: PMC4663121
- DOI: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2015.09.010
Fibronectin-binding protein TDE1579 affects cytotoxicity of Treponema denticola
Abstract
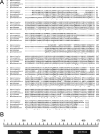
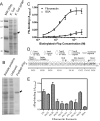
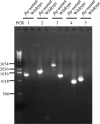
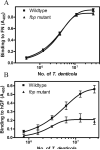
While FbpA, a family of bacterial fibronectin (FN) binding proteins has been studied in several gram-positive bacteria, the gram-negative Treponema denticola, an anaerobic periodontal pathogen, also has an overlooked fbp gene (tde1579). In this research, we confirm that recombinant Fbp protein (rFbp) of T. denticola binds human FN with a Kdapp of 1.5 × 10(-7) M and blocks the binding of T. denticola to FN in a concentration-dependent manner to a level of 42%. The fbp gene was expressed in T. denticola. To reveal the roles of fbp in T. denticola pathogenesis, an fbp isogenic mutant was constructed. The fbp mutant had 51% reduced binding ability to human gingival fibroblasts (hGF). When hGF were challenged with T. denticola, the fbp mutant caused less cell morphology change, had 50% reduced cytotoxicity to hGF, and had less influence on the growth of hGF cells.
Keywords: Fbp; Fibronectin binding protein; Gene mutant; Periodontal disease; Treponema denticola.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Demonstration of factor H-like protein 1 binding to Treponema denticola, a pathogen associated with periodontal disease in humans.Infect Immun. 2005 Nov;73(11):7126-32. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.11.7126-7132.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 16239506 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a novel family of fibronectin-binding proteins with M23 peptidase domains from Treponema denticola.Mol Oral Microbiol. 2010 Dec;25(6):369-83. doi: 10.1111/j.2041-1014.2010.00584.x. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 21040511 Free PMC article.
-
Binding properties and adhesion-mediating regions of the major sheath protein of Treponema denticola ATCC 35405.Infect Immun. 2005 May;73(5):2891-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.5.2891-2898.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15845495 Free PMC article.
-
Treponema denticola major surface protein (Msp): a key player in periodontal pathogenicity and immune evasion.Arch Microbiol. 2025 Jan 18;207(2):36. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-04223-w. Arch Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39825920 Review.
-
Spirochetes at the forefront of periodontal infections.Periodontol 2000. 2005;38:13-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.2005.00108.x. Periodontol 2000. 2005. PMID: 15853935 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Adherence and metal-ion acquisition gene expression increases during infection with Treponema phagedenis strains from bovine digital dermatitis.Infect Immun. 2024 Aug 13;92(8):e0011724. doi: 10.1128/iai.00117-24. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Infect Immun. 2024. PMID: 38940601 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sela MN. Role of Treponema denticola in periodontal diseases. Crit Rev.Oral Biol.Med. 2001;12:399–413. - PubMed
-
- Keulers RA, Maltha JC, Mikx FH, Wolters-Lutgerhorst JM. Attachment of Treponema denticola strains to monolayers of epithelial cells of different origin. Oral Microbiol.Immunol. 1993;8:84–88. - PubMed
-
- Haapasalo M, Hannam P, McBride BC, Uitto VJ. Hyaluronan, a possible ligand mediating Treponema denticola binding to periodontal tissue. Oral Microbiol.Immunol. 1996;11:156–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

