The Association of Serum IL-33 and sST2 with Breast Cancer
- PMID: 26456994
- PMCID: PMC4592729
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/516895
The Association of Serum IL-33 and sST2 with Breast Cancer
Abstract
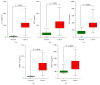
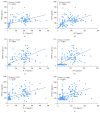
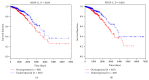
Breast cancer is one of the most common malignant diseases in women. The main cause of death from breast cancer is its metastases at distant sites in the body. Interleukin-33 (IL-33) is a cytokine of the IL-1 family and found overexpressed in various cancers. The aim of the present study was to explore the association of serum IL-33 and sST2 with breast cancer. Here, the serum levels of Interleukin-33 (IL-33) and sST2 were found significantly higher in breast cancer patients than in healthy volunteers. Serum levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), metalloproteinase-11 (MMP-11), and platelet-derived growth factor-C (PDGF-C) were also greater in breast cancer patients compared to healthy volunteers. We found that serum levels of IL-33 or sST2 were positively correlated with the serum levels of VEGF, MMP-11, and PDGF-C. Moreover, breast cancer dataset downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas showed that patients with higher level of MMP-11 or PDGF-C expression had shorter survival time than those with lower level of these proteins. In conclusion, IL-33 and sST2 may serve as noninvasive diagnosis markers for breast cancer. IL-33 and sST2 were significantly associated with MMP-11 or PDGF-C which indicated poor prognosis of breast cancer patients.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

