Endoscopic management of gastrointestinal perforations, leaks and fistulas
- PMID: 26457014
- PMCID: PMC4588076
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i37.10542
Endoscopic management of gastrointestinal perforations, leaks and fistulas
Abstract
Gastrointestinal perforations, leaks and fistulas may be serious and life-threatening. The increasing number of endoscopic procedures with a high risk of perforation and the increasing incidence of leakage associated with bariatric operations call for a minimally invasive treatment for these complications. The therapeutic approach can vary greatly depending on the size, location, and timing of gastrointestinal wall defect recognition. Some asymptomatic patients can be treated conservatively, while patients with septic symptoms or cardio-pulmonary insufficiency may require intensive care and urgent surgical treatment. However, most gastrointestinal wall defects can be satisfactorily treated by endoscopy. Although the initial endoscopic closure rates of chronic fistulas is very high, the long-term results of these treatments remain a clinical problem. The efficacy of endoscopic therapy depends on several factors and the best mode of treatment will depend on a precise localization of the site, the extent of the leak and the endoscopic appearance of the lesion. Many endoscopic tools for effective closure of gastrointestinal wall defects are currently available. In this review, we summarized the basic principles of the management of acute iatrogenic perforations, as well as of postoperative leaks and chronic fistulas of the gastrointestinal tract. We also described the effectiveness of various endoscopic methods based on current research and our experience.
Keywords: Clips; Endoscopic; Fistula; Leak; Management; Perforation; Stent.
Figures
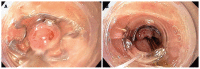

References
-
- Paspatis GA, Dumonceau JM, Barthet M, Meisner S, Repici A, Saunders BP, Vezakis A, Gonzalez JM, Turino SY, Tsiamoulos ZP, et al. Diagnosis and management of iatrogenic endoscopic perforations: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Position Statement. Endoscopy. 2014;46:693–711. - PubMed
-
- Lamazza A, Sterpetti AV, De Cesare A, Schillaci A, Antoniozzi A, Fiori E. Endoscopic placement of self-expanding stents in patients with symptomatic anastomotic leakage after colorectal resection for cancer: long-term results. Endoscopy. 2015;47:270–272. - PubMed
-
- Hady HR, Baniukiewicz A, Luba M, Rogalski P, Dabrowski A, Dadan J. Bronchobiliary fistula as a complication after long-term stenting of hepatic ducts, applied by ERCP after hepatobiliary surgery due to hydatid cyst. Endoscopy. 2011;43 Suppl 2 UCTN:E178–E179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

