Impact of MR Acquisition Parameters on DTI Scalar Indexes: A Tractography Based Approach
- PMID: 26457415
- PMCID: PMC4601730
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137905
Impact of MR Acquisition Parameters on DTI Scalar Indexes: A Tractography Based Approach
Abstract
Acquisition parameters play a crucial role in Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI), as they have a major impact on the values of scalar measures such as Fractional Anisotropy (FA) or Mean Diffusivity (MD) that are usually the focus of clinical studies based on white matter analysis. This paper presents an analysis on the impact of the variation of several acquisition parameters on these scalar measures with a novel double focus. First, a tractography-based approach is employed, motivated by the significant number of clinical studies that are carried out using this technique. Second, the consequences of simultaneous changes in multiple parameters are analyzed: number of gradient directions, b-value and voxel resolution. Results indicate that the FA is most affected by changes in the number of gradients and voxel resolution, while MD is specially influenced by variations in the b-value. Even if the choice of a tractography algorithm has an effect on the numerical values of the final scalar measures, the evolution of these measures when acquisition parameters are modified is parallel.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

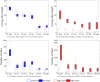
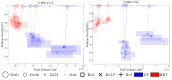
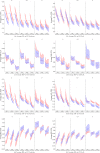

References
-
- Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C. Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. mrm. 1996;111(3):209–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

