Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of frutalin, an α-D-galactose-specific lectin from Artocarpus incisa seeds
- PMID: 26457519
- PMCID: PMC4601592
- DOI: 10.1107/S2053230X15015186
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of frutalin, an α-D-galactose-specific lectin from Artocarpus incisa seeds
Abstract
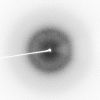
Frutalin is an α-D-galactose-specific carbohydrate-binding glycoprotein with antitumour properties and is a powerful tool for tumour biomarker discovery. The crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of this lectin, which was isolated from Artocarpus incisa seeds, are reported here. Frutalin was purified and submitted to mass-spectrometric analysis. Diverse masses at approximately 16 kDa were observed in the deconvoluted spectra, which support the presence of isoforms. The best frutalin crystals were grown within a week in 0.1 M citric acid pH 3.5 which contained 25% PEG 3350 as a precipitant at 293 K, and diffracted to a maximum resolution of 1.81 Å. The monoclinic crystals belonged to space group I2, with unit-cell parameters a = 76.17, b = 74.56, c = 118.98 Å, β = 96.56°. A molecular-replacement solution was obtained which indicated the presence of four monomers per asymmetric unit. Crystallographic refinement of the structure is in progress.
Keywords: Artocarpus incisa; frutalin; jacalin lectin-related family.
Figures


References
-
- Brando-Lima, A. C., Saldanha-Gama, R. F., Henriques, M. G. M. O., Monteiro-Moreira, A. C. O., Moreira, R. A. & Barja-Fidalgo, C. (2005). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 208, 145–154. - PubMed
-
- Brando-Lima, A. C., Saldanha-Gama, R. F., Pereira, C. R., Villela, C. G., Sampaio, A. L., Monteiro-Moreira, A. C., Henriques, M. G. M. O., Moreira, R. A. & Barja-Fidalgo, C. (2006). Int. Immunopharmacol. 6, 465–472. - PubMed
-
- Campana, P. T., Moraes, D. I., Monteiro-Moreira, A. C. O. & Beltramini, L. M. (2002). Eur. J. Biochem. 269, 753–758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

