Neuronal uptake and propagation of a rare phosphorylated high-molecular-weight tau derived from Alzheimer's disease brain
- PMID: 26458742
- PMCID: PMC4608380
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms9490
Neuronal uptake and propagation of a rare phosphorylated high-molecular-weight tau derived from Alzheimer's disease brain
Abstract
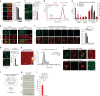
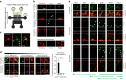
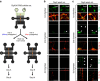
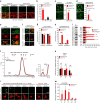
Tau pathology is known to spread in a hierarchical pattern in Alzheimer's disease (AD) brain during disease progression, likely by trans-synaptic tau transfer between neurons. However, the tau species involved in inter-neuron propagation remains unclear. To identify tau species responsible for propagation, we examined uptake and propagation properties of different tau species derived from postmortem cortical extracts and brain interstitial fluid of tau-transgenic mice, as well as human AD cortices. Here we show that PBS-soluble phosphorylated high-molecular-weight (HMW) tau, though very low in abundance, is taken up, axonally transported, and passed on to synaptically connected neurons. Our findings suggest that a rare species of soluble phosphorylated HMW tau is the endogenous form of tau involved in propagation and could be a target for therapeutic intervention and biomarker development.
Figures



Comment in
-
Alzheimer disease: Evidence for trans-synaptic and exo-synaptic tau propagation in Alzheimer disease.Nat Rev Neurol. 2015 Dec;11(12):665. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2015.205. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26526534 No abstract available.
References
-
- Mandelkow E. M. et al.. Tau domains, phosphorylation, and interactions with microtubules. Neurobiol. Aging 16, 355–362 discussion 362–353 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Braak H. & Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 82, 239–259 (1991). - PubMed
-
- Hyman B. T., Van Hoesen G. W., Damasio A. R. & Barnes C. L. Alzheimer's disease: cell-specific pathology isolates the hippocampal formation. Science 225, 1168–1170 (1984). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

