Superoxide dismutase SodB is a protective antigen against Campylobacter jejuni colonisation in chickens
- PMID: 26458797
- PMCID: PMC4654421
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.09.100
Superoxide dismutase SodB is a protective antigen against Campylobacter jejuni colonisation in chickens
Abstract
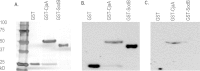
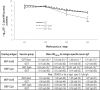
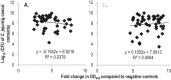
Campylobacter is the leading cause of foodborne diarrhoeal illness in the developed world and consumption or handling of contaminated poultry meat is the principal source of infection. Strategies to control Campylobacter in broilers prior to slaughter are urgently required and are predicted to limit the incidence of human campylobacteriosis. Towards this aim, a purified recombinant subunit vaccine based on the superoxide dismutase (SodB) protein of C. jejuni M1 was developed and tested in White Leghorn birds. Birds were vaccinated on the day of hatch and 14 days later with SodB fused to glutathione S-transferase (GST) or purified GST alone. Birds were challenged with C. jejuni M1 at 28 days of age and caecal Campylobacter counts determined at weekly intervals. Across three independent trials, the vaccine induced a statistically significant 1 log10 reduction in caecal Campylobacter numbers in vaccinated birds compared to age-matched GST-vaccinated controls. Significant induction of antigen-specific serum IgY was detected in all vaccinated birds, however the magnitude and timing of SodB-specific IgY did not correlate with lower numbers of C. jejuni. Antibodies from SodB-vaccinated chickens detected the protein in the periplasm and not membrane fractions or on the bacterial surface, suggesting that the protection observed may not be strictly antibody-mediated. SodB may be useful as a constituent of vaccines for control of C. jejuni infection in broiler birds, however modest protection was observed late relative to the life of broiler birds and further studies are required to potentiate the magnitude and timing of protection.
Keywords: Antibody; Campylobacter jejuni; Chickens; Protection; Superoxide dismutase; Vaccine.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of flagellum-related proteins FliD and FspA as subunit vaccines against Campylobacter jejuni colonisation in chickens.Vaccine. 2016 Apr 4;34(15):1739-43. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.02.052. Epub 2016 Feb 26. Vaccine. 2016. PMID: 26921781 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of live-attenuated Salmonella vaccines expressing Campylobacter antigens for control of C. jejuni in poultry.Vaccine. 2010 Jan 22;28(4):1094-105. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.10.018. Epub 2009 Oct 22. Vaccine. 2010. PMID: 19853682
-
Evaluation of Salmonella-vectored Campylobacter peptide epitopes for reduction of Campylobacter jejuni in broiler chickens.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2011 Mar;18(3):449-54. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00379-10. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21177910 Free PMC article.
-
Design and data analysis of experimental trials to test vaccine candidates against zoonotic pathogens in animals: the case of a clinical trial against campylobacter in broilers.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2012 Oct;11(10):1179-88. doi: 10.1586/erv.12.98. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2012. PMID: 23176651 Review.
-
Vaccines against Campylobacter jejuni.J Infect Dis. 1997 Dec;176 Suppl 2:S183-8. doi: 10.1086/513791. J Infect Dis. 1997. PMID: 9396708 Review.
Cited by
-
A Systematic Review of Campylobacter jejuni Vaccine Candidates for Chickens.Microorganisms. 2021 Feb 15;9(2):397. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9020397. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33671947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The incidence of Campylobacter contamination levels through Chicken-Sashimi Processing steps in A Small-scale Poultry processing plant applying the External stripping method.J Vet Med Sci. 2022 Mar 15;84(3):414-419. doi: 10.1292/jvms.21-0486. Epub 2022 Jan 27. J Vet Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35082194 Free PMC article.
-
IgYs: on her majesty's secret service.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 12;14:1199427. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1199427. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37377972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host-specific differences in the response of cultured macrophages to Campylobacter jejuni capsule and O-methyl phosphoramidate mutants.Vet Res. 2018 Jan 9;49(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13567-017-0501-y. Vet Res. 2018. PMID: 29316981 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Chicken Responses to Glycoconjugate Vaccination Against Campylobacter jejuni.Front Microbiol. 2021 Nov 16;12:734526. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.734526. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34867850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Department for the Environment, Food & Rural Affairs . 2013. Zoonoses report 2013. 〈https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/zoonoses-report-uk-2013〉.
-
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ) Scientific opinion on Campylobacter in broiler meat production: control options and performance objectives and/or targets at different stages of the food chain. EFSA J. 2011;9:2105.
-
- Food Standards Agency . 2015. Cumulative results: first 12 months of retail survey on levels of Campylobacter on chicken. 〈https://www.food.gov.uk/sites/default/files/full-campy-survey-report.pdf〉.
-
- Food Standards Agency . 2009. A UK survey of Campylobacter and Salmonella contamination of fresh chicken at retail sale. 〈http://tna.europarchive.org/20140306205048/http://multimedia. food.gov.〉, 〈uk/multimedia/pdfs/fsis0409 pdf〉.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/D000866/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/D/20320000/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/J500537/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/J004227/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

