Informed shared decision-making supported by decision coaches for women with ductal carcinoma in situ: study protocol for a cluster randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 26458964
- PMCID: PMC4603943
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-015-0991-8
Informed shared decision-making supported by decision coaches for women with ductal carcinoma in situ: study protocol for a cluster randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Women with breast cancer want to participate in treatment decision-making. Guidelines have confirmed the right of informed shared decision-making. However, previous research has shown that the implementation of informed shared decision-making is suboptimal for reasons of limited resources of physicians, power imbalances between patients and physicians and missing evidence-based patient information. We developed an informed shared decision-making program for women with primary ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). The program provides decision coaching for women by specialized nurses and aims at supporting involvement in decision-making and informed choices. In this trial, the informed shared decision-making program will be evaluated in breast care centers.
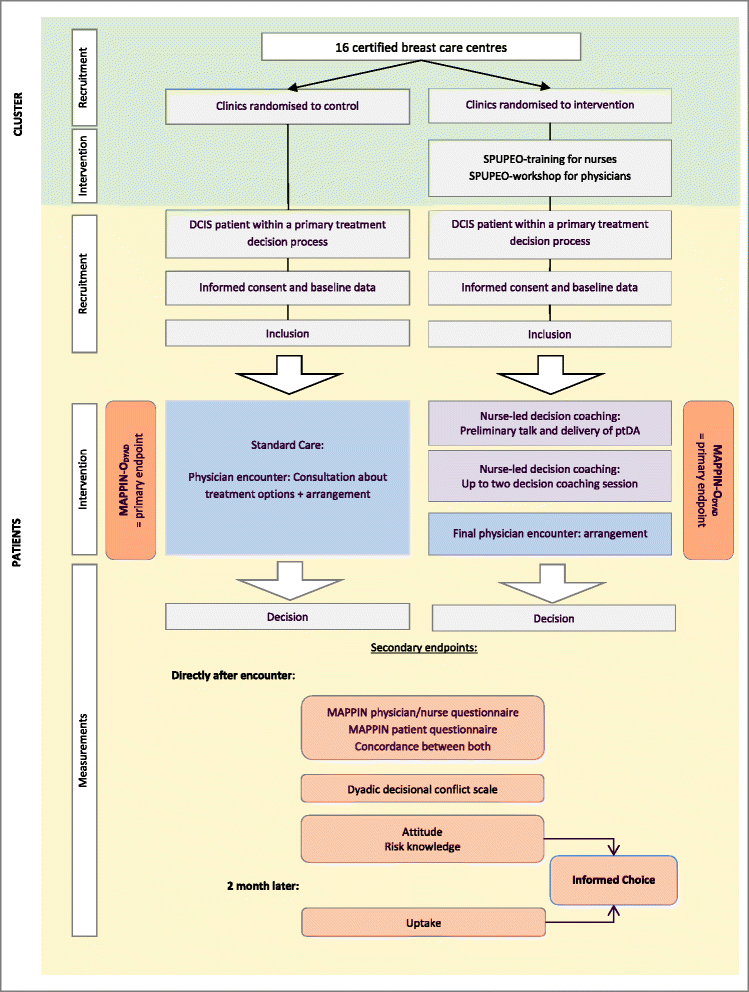
Methods/design: A cluster randomized controlled trial will be conducted to compare the informed shared decision-making program with standard care. The program comprises an evidence-based patient decision aid and training of physicians (2 hours) and specialized breast care and oncology nurses (4 days) in informed shared decision-making. Sixteen certified breast care centers will be included, with 192 women with primary DCIS being recruited. Primary outcome is the extent of patients' involvement in shared decision-making as assessed by the MAPPIN-Odyad (Multifocal approach to the 'sharing' in shared decision-making: observer instrument dyad). Secondary endpoints include the sub-measures of the MAPPIN-inventory (MAPPIN-Onurse, MAPPIN-Ophysician, MAPPIN-Opatient, MAPPIN-Qnurse, MAPPIN-Qpatient and MAPPIN-Qphysician), informed choice, decisional conflict and the duration of encounters. It is expected that decision coaching and the provision of evidence-based patient decision aids will increase patients' involvement in decision-making with informed choices and reduce decisional conflicts and duration of physician encounters. Furthermore, an accompanying process evaluation will be conducted.
Discussion: To our knowledge, this is the first study investigating the implementation of decision coaches in German breast care centers.
Trial registration: Current Controlled Trials ISRCTN46305518 , date of registration: 5 June 2015.
References
-
- Mühlhauser I, Meyer G, Steckelberg A. Patients demand informed participation in medical decision making, but the information data base and structures are not available. Z Allg Med. 2010;86:10–5.
-
- Kreienberg R, Albert U-S, Follmann M, Kopp I, Kühn T, Wöckel A, et al. Interdisciplinary S3-guideline on diagnostics, therapy and follow up of breast cancer. In: German guideline program in oncology. 3rd ed. Berlin: AWMF, DKG, Deutsche Krebshilfe; 2012. http://leitlinienprogramm-onkologie.de/uploads/tx_sbdownloader/S3-Brustk.... Accessed 17 July 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical