Housing Temperature-Induced Stress Is Suppressing Murine Graft-versus-Host Disease through β2-Adrenergic Receptor Signaling
- PMID: 26459348
- PMCID: PMC4637222
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500700
Housing Temperature-Induced Stress Is Suppressing Murine Graft-versus-Host Disease through β2-Adrenergic Receptor Signaling
Abstract
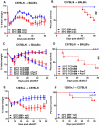
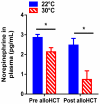
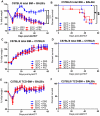
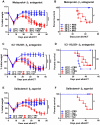
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is the major complication of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation, a potentially curative therapy for hematologic diseases. It has long been thought that murine bone marrow-derived T cells do not mediate severe GVHD because of their quantity and/or phenotype. During the course of experiments testing the impact of housing temperatures on GVHD, we discovered that this apparent resistance is a function of the relatively cool ambient housing temperature. Murine bone marrow-derived T cells have the ability to mediate severe GVHD in mice housed at a thermoneutral temperature. Specifically, mice housed at Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee-mandated, cool standard temperatures (∼ 22°C) are more resistant to developing GVHD than are mice housed at thermoneutral temperatures (∼ 30°C). We learned that the mechanism underlying this housing-dependent immunosuppression is associated with increased norepinephrine production and excessive signaling through β-adrenergic receptor signaling, which is increased when mice are cold stressed. Treatment of mice housed at 22°C with a β2-adrenergic antagonist reverses the norepinephrine-driven suppression of GVHD and yields similar disease to mice housed at 30°C. Conversely, administering a β2-adrenergic agonist decreases GVHD in mice housed at 30°C. In further mechanistic studies using β2-adrenergic receptor-deficient (β2-AR(-/-)) mice, we found that it is host cell β2-AR signaling that is essential for decreasing GVHD. These data reveal how baseline levels of β-adrenergic receptor signaling can influence murine GVHD and point to the feasibility of manipulation of β2-AR signaling to ameliorate GVHD in the clinical setting.
Copyright © 2015 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Hahn T, McCarthy PL, Jr., Zhang MJ, Wang D, Arora M, Frangoul H, Gale RP, Hale GA, Horan J, Isola L, Maziarz RT, van Rood JJ, Gupta V, Halter J, Reddy V, Tiberghien P, Litzow M, Anasetti C, Pavletic S, Ringden O. Risk factors for acute graft-versus-host disease after human leukocyte antigen-identical sibling transplants for adults with leukemia. JClin Oncol. 2008;26:5728–5734. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Palathumpat V, Dejbakhsh-Jones S, Holm B, Strober S. Different subsets of T cells in the adult mouse bone marrow and spleen induce or suppress acute graft-versus-host disease. J Immunol. 1992;149:808–817. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

