Innate lymphoid cells in intestinal immunity and inflammation
- PMID: 26459449
- PMCID: PMC11108440
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-015-2055-3
Innate lymphoid cells in intestinal immunity and inflammation
Abstract
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are a new and distinct family of innate immune cells that play an important role in immunity and inflammation. In this review, we focus on the role of ILCs in mucosal tissues, especially in the gut, in health and disease. ILCs support intestinal homeostasis by protecting the intestine from pathogens, contributing to the development of gut lymphoid tissue, and helping to repair injuries. By cooperating with epithelial cells and other innate and adaptive immune cells, ILCs participate in the control of pathogens and tolerance of commensal bacteria. The development and maintenance of ILCs are influenced by nutrients and metabolites sourced from diet and/or gut bacteria. ILCs have been shown to be involved in host metabolism and to participate in various diseases of the intestine including infectious and chronic inflammatory diseases, and cancer. Thus, the elucidation of ILC biology provides an exciting potential for development of novel therapeutic means to modulate immune responses in various disease settings.
Keywords: Commensals; Diet; Homeostasis; Metabolism; Nutrition.
Figures
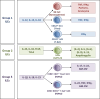
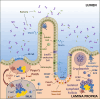
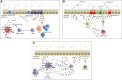
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

