Catalogue of abrupt shifts in Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change climate models
- PMID: 26460042
- PMCID: PMC4629371
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1511451112
Catalogue of abrupt shifts in Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change climate models
Abstract
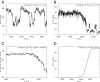
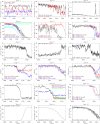
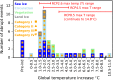
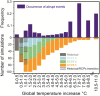
Abrupt transitions of regional climate in response to the gradual rise in atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations are notoriously difficult to foresee. However, such events could be particularly challenging in view of the capacity required for society and ecosystems to adapt to them. We present, to our knowledge, the first systematic screening of the massive climate model ensemble informing the recent Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change report, and reveal evidence of 37 forced regional abrupt changes in the ocean, sea ice, snow cover, permafrost, and terrestrial biosphere that arise after a certain global temperature increase. Eighteen out of 37 events occur for global warming levels of less than 2°, a threshold sometimes presented as a safe limit. Although most models predict one or more such events, any specific occurrence typically appears in only a few models. We find no compelling evidence for a general relation between the overall number of abrupt shifts and the level of global warming. However, we do note that abrupt changes in ocean circulation occur more often for moderate warming (less than 2°), whereas over land they occur more often for warming larger than 2°. Using a basic proportion test, however, we find that the number of abrupt shifts identified in Representative Concentration Pathway (RCP) 8.5 scenarios is significantly larger than in other scenarios of lower radiative forcing. This suggests the potential for a gradual trend of destabilization of the climate with respect to such shifts, due to increasing global mean temperature change.
Keywords: CMIP5; IPCC; abrupt climate change; climate change; critical transitions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change . In: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Stocker TF, et al., editors. Cambridge Univ Press; New York: 2013.
-
- Levermann A, et al. Potential climatic transitions with profound impact on Europe—Review of the current state of six ‘tipping elements of the climate system.’. Clim Change. 2012;110(3):845–878.
-
- Collins M, et al. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Cambridge Univ Press; New York: 2013. Long-term climate change: Projections, commitments and irreversibility; pp. 1029–1076.
-
- Rockström J, et al. A safe operating space for humanity. Nature. 2009;461(7263):472–475. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

