Role of the Toll‑like receptor 3 signaling pathway in the neuroprotective effect of sevoflurane pre‑conditioning during cardiopulmonary bypass in rats
- PMID: 26460219
- PMCID: PMC4758330
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4420
Role of the Toll‑like receptor 3 signaling pathway in the neuroprotective effect of sevoflurane pre‑conditioning during cardiopulmonary bypass in rats
Abstract
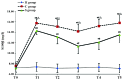
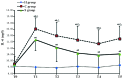
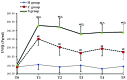
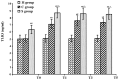
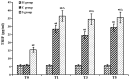
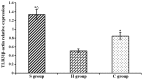
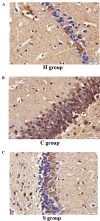
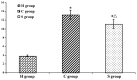
The aim of the present study was to explore the roles and possible molecular mechanism of the alleviating effect of sevoflurane pre‑treatment on the extracorporeal circulation and to investigate the possible involvement of the Toll‑like receptor (TLR3) signaling pathway. A total of 64 male Sprague Dawley rats were randomly divided into three groups: The sham operation group (H group; n=8), cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) group (C group; n=24) and sevoflurane pre‑conditioning group (S group; n=32). The C group was subjected to tracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation, vessel puncture and catheter placement in the right femoral artery and right internal jugular vein, while no CPB was performed in the H group. The S group was pre‑treated with 2.4% sevoflurane for 1 h prior to establishing the CPB model. The CPB in the C and S groups was performed for 1 h. Blood of the rats was analyzed and clinical parameters were detected prior to, during and at various time‑points after CPB. In addition, eight rats from the C and S groups each were sacrificed at these time‑points and brain tissue samples were analyzed. The levels of the brain damage‑specific protein S100‑β as well as IL‑6 and IFN‑β in the serum were detected by ELISA; furthermore, the expression levels of TLR3 and TIR‑domain‑containing adapter‑inducing interferon‑β (TRIF) in the left hippocampus were assessed by ELISA and/or western blot analysis. The right hippocampus was assessed for neuronal apoptosis by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling assay. The mean arterial pressure, heart rate and hematocrit were significantly decreased following CPB (P<0.05), while there was no significant changes in any other clinical parameters. The serum levels of S100‑β and IL‑6 in the C group were significantly increased compared with those in the H group (P<0.05), which was attenuated by sevoflurane‑pre‑treatment. Compared with the H group, the serum levels of IFN‑β as well as hippocampal protein levels of TLR3 and TRIF were significantly increased in the C group during and after CPB (P<0.05), which was markedly aggravated in the S group (P<0.05). The number of apoptotic hippocampal neurons, although being generally low, was significantly increased in the C group compared with that in the H group (P<0.05), while apoptosis was significantly attenuated by sevoflurane‑pre‑treatment (P<0.05). The present study therefore concluded that 2.4% sevoflurane pre‑treatment has a protective effect on the rat brain against CPB‑induced injury, which may be mediated via the TLR3 signaling pathway through upregulating the expression levels of anti‑inflammatory and downregulating pro‑inflammatory proteins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of TLR3 and TLR9 Signaling Pathway on Brain Protection in Rats Undergoing Sevoflurane Pretreatment during Cardiopulmonary Bypass.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:4286738. doi: 10.1155/2017/4286738. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 29445737 Free PMC article.
-
α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist inhibits the damage of rat hippocampal neurons by TLR4/Myd88/NF‑κB signaling pathway during cardiopulmonary bypass.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Oct;16(4):4770-4776. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7166. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28791395 Free PMC article.
-
κ‑opioid receptor agonist U50488H attenuates postoperative cognitive dysfunction of cardiopulmonary bypass rats through the PI3K/AKT/Nrf2/HO‑1 pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Apr;23(4):293. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.11933. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33649775 Free PMC article.
-
Ac2-26 activated the AKT1/GSK3β pathway to reduce cerebral neurons pyroptosis and improve cerebral function in rats after cardiopulmonary bypass.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 May 21;24(1):266. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-03909-9. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 38773462 Free PMC article.
-
S100 and S100β: biomarkers of cerebral damage in cardiac surgery with or without the use of cardiopulmonary bypass.Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc. 2014 Oct-Dec;29(4):630-41. doi: 10.5935/1678-9741.20140084. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc. 2014. PMID: 25714218 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
κ-opioid receptor agonists may alleviate intestinal damage in cardiopulmonary bypass rats by inhibiting the NF-κB/HIF-1α pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Jul;20(1):325-334. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8685. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32509012 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of TLR3 and TLR9 Signaling Pathway on Brain Protection in Rats Undergoing Sevoflurane Pretreatment during Cardiopulmonary Bypass.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:4286738. doi: 10.1155/2017/4286738. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 29445737 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen‑rich solution against myocardial injury and aquaporin expression via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway during cardiopulmonary bypass in rats.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Aug;18(2):1925-1938. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9198. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29956781 Free PMC article.
-
α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist attenuates the cerebral injury in a rat model of cardiopulmonary bypass by activating the Akt/GSK3β pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Dec;16(6):7979-7986. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7600. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28944927 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine attenuates acute kidney injury in children undergoing congenital heart surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass by inhibiting the TLR3/NF-κB signaling pathway.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Apr 15;13(4):2763-2773. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34017439 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mei B. Study of brain injury and brain protection during cardiopulmonary bypass progress. Zhong Guo Ti Wai Xun Huan Za Zhi. 2010;8:125–127. In Chinese.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

