Intrinsic Age-Dependent Changes and Cell-Cell Contacts Regulate Nephron Progenitor Lifespan
- PMID: 26460946
- PMCID: PMC4615609
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.09.009
Intrinsic Age-Dependent Changes and Cell-Cell Contacts Regulate Nephron Progenitor Lifespan
Abstract
During fetal development, nephrons of the metanephric kidney form from a mesenchymal progenitor population that differentiates en masse before or shortly after birth. We explored intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms controlling progenitor lifespan in a transplantation assay that allowed us to compare engraftment of old and young progenitors into the same young niche. The progenitors displayed an age-dependent decrease in proliferation and concomitant increase in niche exit rates. Single-cell transcriptome profiling revealed progressive age-dependent changes, with heterogeneity increasing in older populations. Age-dependent elevation in mTor and reduction in Fgf20 could contribute to increased exit rates. Importantly, 30% of old progenitors remained in the niche for up to 1 week post engraftment, a net gain of 50% to their lifespan, but only if surrounded by young neighbors. We provide evidence in support of a model in which intrinsic age-dependent changes affect inter-progenitor interactions that drive cessation of nephrogenesis.
Keywords: Fgf20; aging; kidney; mTor; nephron; stem cells.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
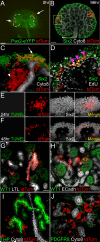

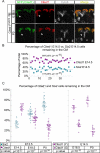
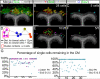
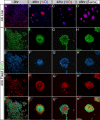

Comment in
-
The Life Cycle of the Nephron Progenitor.Dev Cell. 2015 Oct 12;35(1):5-6. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.09.023. Dev Cell. 2015. PMID: 26460940
-
Stem cells: Young nephron progenitors might extend the lifespan of old progenitors.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015 Dec;11(12):690. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2015.179. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 26526402 No abstract available.
References
-
- Al-Awqati Q, Goldberg MR. Architectural patterns in branching morphogenesis in the kidmey Kidney International. 1998;54:1832–1842. - PubMed
-
- Barker DJ, Shiell AW, Barker ME, Law CM. Growth in utero and blood pressure levels in the next generation. Journal of hypertension. 2000;18:843–846. - PubMed
-
- Bertram JF, Douglas-Denton RN, Diouf B, Hughson MD, Hoy WE. Human nephron number: implications for health and disease. Pediatr Nephrol. 2011;26:1529–1533. - PubMed
-
- Bottcher RT, Pollet N, Delius H, Niehrs C. The transmembrane protein XFLRT3 forms a complex with FGF receptors and promotes FGF signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6:38–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

