Effects of a novel Nodal-targeting monoclonal antibody in melanoma
- PMID: 26460952
- PMCID: PMC4741437
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.6049
Effects of a novel Nodal-targeting monoclonal antibody in melanoma
Abstract
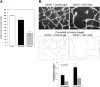
Nodal is highly expressed in various human malignancies, thus supporting the rationale for exploring Nodal as a therapeutic target. Here, we describe the effects of a novel monoclonal antibody (mAb), 3D1, raised against human Nodal. In vitro treatment of C8161 human melanoma cells with 3D1 mAb shows reductions in anchorage-independent growth and vasculogenic network formation. 3D1 treated cells also show decreases of Nodal and downstream signaling molecules, P-Smad2 and P-ERK and of P-H3 and CyclinB1, with an increase in p27. Similar effects were previously reported in human breast cancer cells where Nodal expression was generally down-regulated; following 3D1 mAb treatment, both Nodal and P-H3 levels are reduced. Noteworthy is the reduced growth of human melanoma xenografts in Nude mice treated with 3D1 mAb, where immunostaining of representative tumor sections show diminished P-Smad2 expression. Similar effects both in vitro and in vivo were observed in 3D1 treated A375SM melanoma cells harboring the active BRAF(V600E) mutation compared to treatments with IgG control or a BRAF inhibitor, dabrafenib. Finally, we describe a 3D1-based ELISA for the detection of Nodal in serum samples from cancer patients. These data suggest the potential of 3D1 mAb for selecting and targeting Nodal expressing cancers.
Keywords: ELISA; Nodal; antibody; cancer; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Mary JC Hendrix, Elisabeth A Seftor and Richard EB Seftor hold a patent for targeting Nodal.
Figures






References
-
- Song X, Zhao Z, Barber B, Farr AM, Ivanov B, Novich M. Overall survival in patients with metastatic melanoma. Curr Med Res Opin. 2015;31:987–991. - PubMed
-
- Gogas HJ, Kirkwood JM, Sondak VK. Chemotherapy for metastatic melanoma: time for a change? Cancer. 2007;109:455–464. - PubMed
-
- Han SF, Liu P, Zhang W, Bu L, Shen M, Li H, Fan YH, Cheng K, Cheng HX, Li CX, Jia GL. The opposite-direction modulation of CD4+CD25+ Tregs and T helper 1 cells in acute coronary syndromes. Clin Immunol. 2007;124:90–97. - PubMed
-
- Coit DG, Thompson JA, Andtbacka R, Anker CJ, Bichakjian CK, Carson WE, 3rd, Daniels GA, Daud A, Dimaio D, Fleming MD, Gonzalez R, Guild V, Halpern AC, et al. Melanoma, version 4. 2014. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2014;12:621–629. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

