Differential hippocampal shapes in posterior cortical atrophy patients: A comparison with control and typical AD subjects
- PMID: 26461053
- PMCID: PMC4949635
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.22999
Differential hippocampal shapes in posterior cortical atrophy patients: A comparison with control and typical AD subjects
Abstract
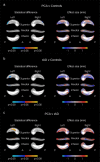
Posterior cortical atrophy (PCA) is a neurodegenerative syndrome characterized by predominant visual deficits and parieto-occipital atrophy, and is typically associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology. In AD, assessment of hippocampal atrophy is widely used in diagnosis, research, and clinical trials; its utility in PCA remains unclear. Given the posterior emphasis of PCA, we hypothesized that hippocampal shape measures may give additional group differentiation information compared with whole-hippocampal volume assessments. We investigated hippocampal volume and shape in subjects with PCA (n = 47), typical AD (n = 29), and controls (n = 48). Hippocampi were outlined on MRI scans and their 3D meshes were generated. We compared hippocampal volume and shape between disease groups. Mean adjusted hippocampal volumes were ∼ 8% smaller in PCA subjects (P < 0.001) and ∼ 22% smaller in tAD subject (P < 0.001) compared with controls. Significant inward deformations in the superior hippocampal tail were observed in PCA compared with controls even after adjustment for hippocampal volume. Inward deformations in large areas of the hippocampus were seen in tAD subjects compared with controls and PCA subjects, but only localized shape differences remained after adjusting for hippocampal volume. The shape differences observed, even allowing for volume differences, suggest that PCA and tAD are each associated with different patterns of hippocampal tissue loss that may contribute to the differential range and extent of episodic memory dysfunction in the two groups.
Keywords: Alzheimer; Alzheimer's disease; PCA; atrophy; classifier; hippocampus; morphometry; shape; support vector machine.
© 2015 The Authors Human Brain Mapping Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Addis DR, Moscovitch M, Crawley AP, McAndrews MP (2004): Recollective qualities modulate hippocampal activation during autobiographical memory retrieval. Hippocampus 14:752–762. - PubMed
-
- Alladi S, Xuereb J, Bak T, Nestor P, Knibb J, Patterson K, Hodges JR (2007): Focal cortical presentations of Alzheimer's disease. Brain 130:2636–2645. - PubMed
-
- Baxter DM, Warrington EK (1994): Measuring dysgraphia: A graded‐difficulty spelling test. Behav Neurol 7:107–116. - PubMed
-
- Benson DF, Davis RJ, Snyder BD (1988): Posterior Cortical Atrophy. Arch Neurol 45:789–793. - PubMed
-
- Boccardi M, Bocchetta M, Apostolova LG, Barnes J, Bartzokis G, Corbetta G, DeCarli C, deToledo‐Morrell L, Firbank M, Ganzola R, Gerritsen L, Henneman W, Killiany RJ, Malykhin N, Pasqualetti P, Pruessner JC, Redolfi A, Robitaille N, Soininen H, Tolomeo D, Wang L, Watson C, Wolf H, Duvernoy H, Duchesne S, Jack CR, Frisoni GB (2015): Delphi definition of the EADC‐ADNI Harmonized Protocol for hippocampal segmentation on magnetic resonance. Alzheimers Dement 11:126–138. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

